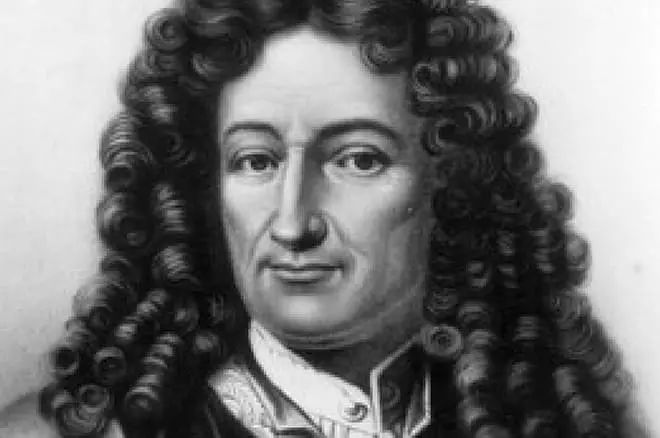
Biography
Surely many still with school bench remember that on the pages of textbooks on algebra you can find the name Leibnitsa, and sometimes his portrait. But not everyone knows that this person not only came up with an integral sign and mathematical formulas, but also made discoveries in other scientific fields. Unfortunately, Leibniz did not receive due respect for his merits in life, but his name became immortal, and the teachings of this philosopher became fundamental for future generations.Childhood and youth
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was born on June 21 (July 1) of 1646, in the administrative center of the land of Lower Saxony - Hanover. Gottfried grew up in the family of a professor of Serbo-Luzhitsky origin, which was not far from the philosophical teaching: for 12 years, the main breadwinner in the house taught a special form of knowing the world and positioned himself as a public professor of morality.
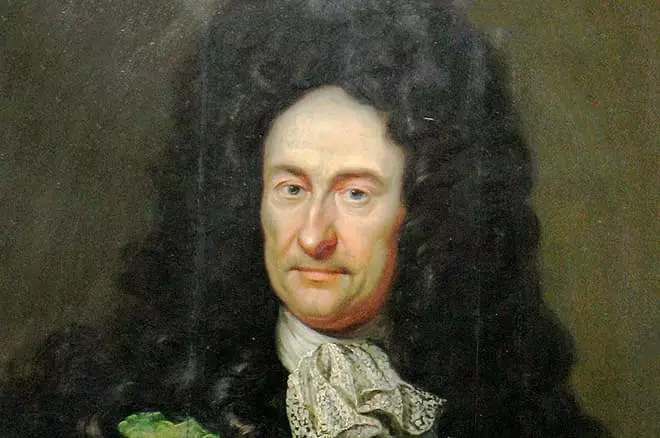

His third spouse Katerina Shmukk, the daughter of a high-ranking lawyer, by nationality - purebred German. Gottfried was a kid kissed by God: From early childhood, the boy showed his genius, so the leibrates tried to develop the curiosity of a little son. Already then there was no doubt that their offspring would become a great scientist who would present the useful inventions to this world.
The father of the gifted boy instilled in Gottfreed Love for literature, so Leibniz swallowed books one by another, reading historical stories about the great kings and brave knights. Unfortunately, Leibniz-Sr. died when the boy was not and seven years old, but the parent left after herself a big library, which became a favorite place in the young Gottfried.

One day the future philosopher and the scientist stumbled upon two manuscripts, once left by the student. These were the works of the Ancient Roman historian Libya and the chronological treasury of Calvia. The last author, the young leibunis read without difficulty, but the understanding of Libya turned out to be difficult for Gottfried, because the old book was written using elevated rhetoric and equipped with ancient engravings.
But Leibniz, who is not accustomed to surrender, re-read the works of the philosopher, until she understood the essence of the dictionary written without using the dictionary. Also, the young man studied German and Latin, ahead of the mental development of his peers. Labitsa teacher noticed that his ward was not followed by a school program, but runs forward, putting into the piggy bank of his knowledge of the writer's writer, who should pay attention to, being a student of senior classes.

Therefore, the teacher who believed that Gottfried should be removed Libya's books far away, argued the boosters of the young man, that it is necessary to pay attention to the self-education of the Leibnian and instill the love of the love of Humanist Komensky and theologian Martin Luther. But, by a happy coat of circumstances, the nobleman passing by, heard this conversation and squinting the teacher for the fact that he merit all with one measurement.
Consequently, no one forbade the Leibnitsa independently replenish the luggage of knowledge, because passerby - a nobleman, an entitled to the genius of Leibnitsa, demanded from his parents to give the key from the Father's Library. Thus, the young man with impatience of the young man touched the works of the ancient scholars of Cicero, Plato, Seneki, Plinia.

Leibniz studied in a prestigious educational institution - the Leipzig School of St. Thoma. There, a young man demonstrated his mental abilities to teachers. He quickly solved mathematical tasks and even showed literary talent. On the day of the Holy Trinity, the student who had to read a festive speech was ill, so this duty was entrusted to the leibitus.
Gottfried managed overnight to compose a work in Latin. Moreover, he was able to build a poem out of five drats, having achieved the desired sound of words. The teachers propheted the boy, which was then only 1 years old, a great future.
Next, 14 (15) -E-year-old Gotfride continued to nibble granite science no longer at school, but at the University of Leipzig. There he was fond of philosophy - the writings of Kepler and Galilee. Two years later, Leibniz was transferred to the University of Jena, where he began to go in an in-depth mathematics.
Among other things, the young man began to get involved in jurisprudence, because he believed that the science that the goddess of the Femid was fading in a further life. In the 1663rd Leibniz received a bachelor's degree, and a year later, a master's degree in philosophy.
Doctrine
The first treatise "On the principle of individualization" of Leibniz wrote in 1663. Few people know, but after graduating from the University, Gottfried became a hired alchemist. The fact is that Leibniz has heard about the alchemical community in Nuremberg and decided to act a cunning: he discharged the most incomprehensible formulas from the books of famous alchemists and brought his essay by the Chairmen of the Order of Rosenkreyers.

Adherents of mystical teachings were amazed by Gotfreed's knowledge and proclaimed him by the adept. The scientist confessed that he was not tormented by remorse, the future mathematician went for such a step because it was so told by his unpretentious curiosity.
In 1667, young Leibniz began to engage in publicist activities and succeeded in philosophical and psychological teaching. It is worth saying that when the conversation about the unconscious is coming, then many remember Sigmund Freud, but it was Leibniz who put forward the concept of unconscious small perceptions, ahead of German psychoanalyst for two hundred years. In 1705, "new experiments on human understanding" were written, and in five years later the philosophical work called "Monadology" (1710).

The philosopher created his own synthetic system, believed that the whole diverse world consists of certain substances - monads that exist separately from each other, and they, in turn, are a spiritual unit of being. Moreover, from his point of view, the world is not something inexplicable, because it is quite cognized, and the problem of truth requires rational interpretation. For the teachings, the Leibnia Higher Monad is a creator who has established a certain world order, and the criterion of truth advocated logical evidence.

Gottfried considered Genesis as something harmonious, but he also tried to overcome the contradictions of good and evil. The philosophical works of the Leibnia influenced Schelling and Schopenhauer, but Voltaire considered his doctrine about the "theotition or justification of God" (1710), which describes three stages of evil, absurd.
Mathematics and science
Because of his position in the service of the Mainz Kurfürst, Gotfreed had to travel in Europe. During these connectors, he met the Dutch inventor Christian Guigens, who agreed to teach him mathematics.

In 1666, Gottfried becomes the author of the composition "On the art of combinatorics", and he also conceived a project about the mathematization of logic. We can say that Leibniz looked back again, because this scientist stood at the sources of the computer and computer science.
In 1673, he came up with a desktop computing, leading automatic recording of the processed numbers in a decimal system of calculus. The device is referred to as an arithmometer leiby (drawings of the arithmometer are found in Leonardo da Vinci manuscripts). The fact is that Leibnitsa annoyed that his buddy Christians spends a lot of time by adding numbers, while Gottfried himself believed that he would add, take away, share and multiply - this was the servants.
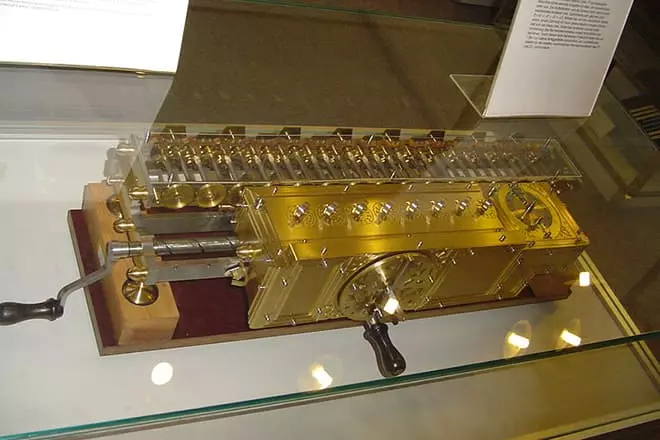
The leibness arithmometer surpassed Pascal's counting machine. It is noteworthy that one copy of the computing device fell into the hands of Peter I, which, surprised by the device, hurried to give this miracle to the Chinese emperor.
The acquaintance of the king, who burned the window to Europe, and the German scientist occurred in 19997, and this meeting was random. After long conversations, Leibniz received from Peter, the monetary remuneration and title of the secret advisor of justice. But earlier, after the defeat of the Russian troops in the battle on Narva, Leibniz was composed of a laudatory Odea Karla XII, where he expressed the hope that Sweden would spread his borders from Moscow to Amur.
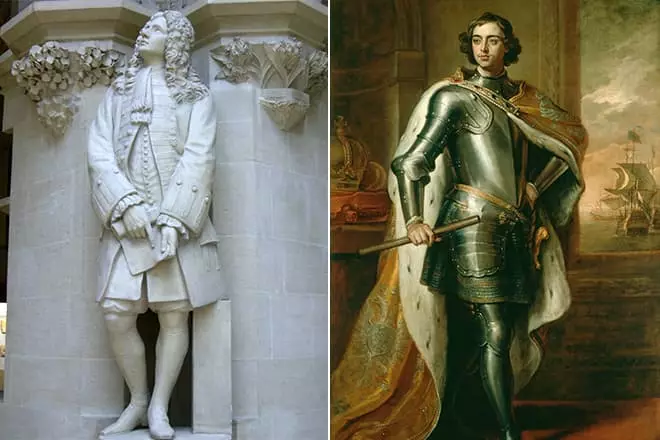

But then he confessed that he had happiness to be a friend of the great Russian monarch, and thanks to Leibnitsa Peter I approved the creation of the Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg. From the biography of Gotfrida, it is known that in 1708 he had a dispute with the author of the law of the World History of Isaac Newton. Leibniz published his mathematical discovery of a differential calculus system, but Newton, who became acquainted with this scientific work, accused a colleague on the workshop in the stealing of ideas and plagiarism.
Isaac stated that he came to the same results 10 years ago, but did not publish his works. Leibniz did not denote that he had once studied Newton's manuscript, but he came to the same results independently. In addition, the German came up with a more convenient symbolism, which mathematicians use to this day.
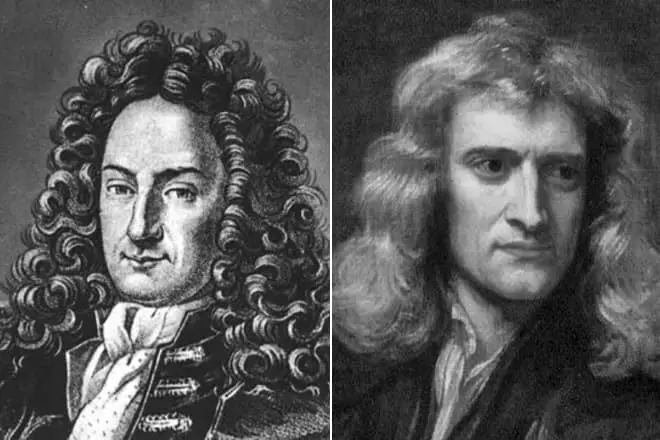

The controversy between Newton and Leibniz continued until 1713, this dispute became a grain at the beginning of a pan-European "priority war", and in the cities there were anonymous brochures that defended the priority of one of the participants in the conflict. This confrontation has become known as "the most shameful squabble in the entire history of mathematics."
Because of the hosts, two scientists lied the English mathematical school, and some opening Newton were ignored and the public became known only after many years. In addition to mathematics, physics and psychology, Leibniz studied biology, (the scientist put forward the idea of organic systems as integrity), and also succeeded in linguistics and jurisprudence.
Personal life
Leibnic is often called the comprehensive mind of humanity, but Gottfried, full of ideas, did not always bring the work started to the end. It's difficult to judge about the nature of the scientist, since his contemporaries described the portrait of a scientist in different ways. Some said that he was a boring and unpleasant person, others were given exclusively positive characteristics.
Gottfried, adhering to his own philosophy, was an optimist and humanist, which even during the conflict with Isaac Newton did not say a bad word to the opponent. But Leibniz was quick-tempered and injured, but he quickly came to his senses and often laughed, even if it was insincere emotions. Nevertheless, the scientist had a vice, which he himself recognized: Sometimes the mathematician was a stingy and korestolobiv.

Leibniz dressed neat and wore a black wig, because it was so dictated by the fashion of that time. In a meal, the scientist was not picky, and wine drank rarely, often on holidays. But even in this burning drink from grapes, Gottfried mixed sugar, as he adored sweet.
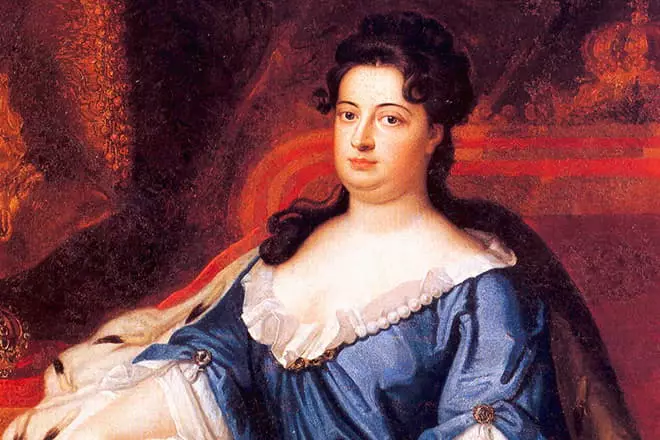
As for the amournal relationship, there is little information about the novels of Gottfried, and some biographers are confident that there was one woman in the life of a scientist - science. But he started a warm friendship with the Prussian Queen Sofia Charlotte Hannover, however, these relationships did not go beyond the framework of Platonic. In 1705, Sofia died, and Leibniz could not accept the rest of his life with what he had happened, after the death of his beloved, he did not find the ladies, which would have touched his heart.
Death
The last years of life, the Leibnitsa was tense, since his relationship with the current English king was not charged: they looked at the great scientist as a court historically, and the ruler, confident that he spends extra money to pay for the work of Labitsa, all the time expressed his discontent all the time. Therefore, surrounded by the scientist was intrigue of the courtiers and attacks on the part of the Church.

But, despite the futility of being, Gottrid continued to engage in favorite science. Because of the sedentary lifestyle, the scientist had a gout and rheumatism, but the genius did not trust his health to the doctors, and enjoyed only one medicine donated by a friend. In addition, the Leibniz had vision problems, as the philosopher in old age did not lose love for reading.
On November 14, 1716, Leibniz did not calculate the dose of therapeutic drug and felt ailment. Having arrived, seeing the state of mathematics, he himself went to the pharmacy, but did not have time - Gottfried Leibniz died. Behind the coffin of the sage, who presented the world unprecedented discovery, only one person went - his secretary.
Discoveries
- 1673 - arithmometer
- 1686 - symbol for integral
- 1692 - the concept and equation of the envelope of a single-parameter family of curves
- 1695 - indicative function in the most general form
- 1702 - Receipt of decomposition of rational fractions on the sum of the simplest
