Biography
John Von Neuman - a famous scientist and a scholars specializing in mathematics, physics, economics, statistics and computing technology. The author of 150 works became a pioneer to apply operator theory to quantum mechanics and a central figure in the development of concepts of cellular automata, a universal designer and a digital computer. As a member of the Manhattan project, von Neumanov created mathematical models used in nuclear weapons, and later became a consultant to the government group assessing the arms system.Childhood and youth
A person who familiar to the scholar world under the name of John von Neuman, was born on December 28, 1903 in the capital of Hungary, Budapest, in a prosperous Jewish family. Father Max Neuman, doctor of jurisprudence, worked at the bank, and Margaret Cann's mother led the farm and raised three children. A future scientist since childhood showed incredible abilities: in the 6th age he freely divided and multiplied in his mind long numbers and spoke in ancient Greek.

After receiving the first lessons from the governess, the boy met the differential and integral calculus and studied several volumes of history written by Wilhelm Onken. When Von Neumanan was 10 years old, the parents sent him to the best school of Budapest, which made up not one generation of great minds, and hired private tutors to develop and strengthen the knowledge of the Son.
By 19 years, the young man issued a publication in which the current definition of sequence numbers gave, replaced the wording of George Kantor, and won the Eötvös National Award. Father admired the mind of the young background of Nymanan, but did not see productive use of his knowledge. Going to a compromise, the young man agreed to become a chemist engineer and has studied the necessary items at the University of Berlin for 2 years. In 1923 he entered the Higher Technical School of Zurich, while at the same time becoming a candidate of mathematical sciences in Elte.

After graduating from both educational institutions, the young man continued to improve and passed the entrance exams in Gottingen University of George-Augustus, received a scholarship of the Rockefeller Foundation and hit the Department of David Hilbert, who became anxiology of Euclidean geometry and creating a functional analysis.
In 1926, von Neumanov received a doctoral degree in mathematics and became the Lecturer of Berlin University. Judging by the photo, a novice teacher organically fit into the college atmosphere and led classes, constantly being at the board covered by formulas and calculations. By the end of 1929, a young privat-associate professor published 32 scientific articles and moved to the team of the highest educational institution of the city of Princeton, the United States, where he worked until the end of his life.
Scientific activity
The first major labor von Neumanna became a dissertation describing a new approach to formalizing the theory of sets. The scientist formulated 2 methods of getting rid of Russell Paradox, introducing the terms "base axiom" and "class".

The base axiom meant the construction of sets from the bottom up and the organization of the sequence, where each set preceded to another or went after it. To demonstrate the absence of contradictions, John applied the concept of the internal model method, which became a fundamental tool in the work on the theory of sets.
To describe the 2nd method, the exclusion of the mathematical paradox von Neumann identified the set with the concept of class and demonstrated the likelihood of building a group of sets that do not belong to themselves.

In the articles released at the end of the 1920s, von Neumann distinguished himself by the contribution to the ergodic theory, and then crossed the questions of quantum mechanics and its mathematical justification. He wrote a number of scientific essays in this area and proved that quantum systems are nothing more than a point in the Hilbert space, over which linear operators are located, consisting of conventional physical quantities.
Proof Von Neumanan gave the start of the studies to approve that quantum physics either needs the concept of reality, or should include non-locality in an explicit violation of the special theory of relativity.

Arguing about the mathematical principles of quantum mechanics, John von Neumann analyzed the so-called measurement theory and concluded that the physical universe can be due to a universal wave function.
This prompted the researcher to open the fundamental principles of functional analysis, the creation of the theory of limited operators and the introduction of the concept of "direct integral", which brought John a Bochra Memorial Prize in 1938.
One of the numerous merit of the Hungarian mathematician was the proof of the "Minimax Theorem", the necessary element of the emerging game theory. The scientist understood that a pair of strategies were present in the zero-sum games, allowing each participant to minimize their own maximum losses. The player must take into account all the existing opponent's reactions and play the optimal strategy that will become the guarantor of minimizing its maximum loss.

Between 1937 and 1939, Von Neuman studied the theory of lattices, where the object of the study was partially ordered sets, in which every 2 elements had the largest lower boundary and the smallest top, and in the process proved the following basic representation theorem.
In addition, von Neumann invested in the development of the economy, printed the works on the intellectual and mathematical level of this discipline. Relying on the results, John invented the theory of duality in linear programming and became the author of the first inner point method, based on the system of pride.
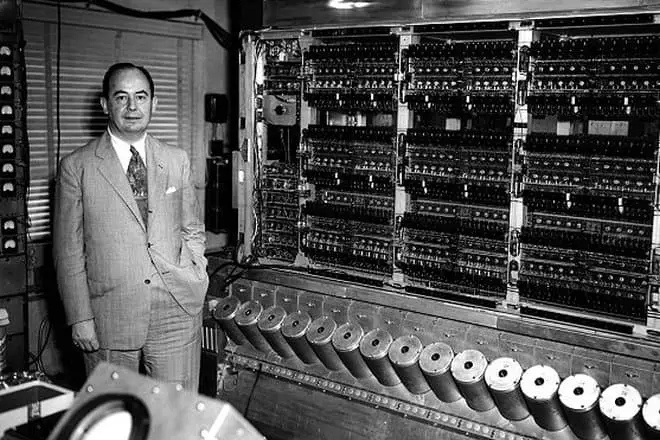
Another merit of John von Nymanan is considered to be the work in the field of computer science, dedicated to the creation and description of the computer architecture, where at the base lay binary coding, homogeneity and memory addressability, conditional transition and consistent control programming. Using the first generation computers, John, in collaboration with Alan Turing, explored the problems of the philosophy of artificial intelligence, but in this matter it was far from advanced.
In the hydrodynamics of the main invention, the background of Neumanan is recognized as an artificial viscosity definition algorithm, which helped in understanding the phenomenon of shock waves. The scientist opened a classic flow solution and applied computer simulation for ballistic studies in this area.
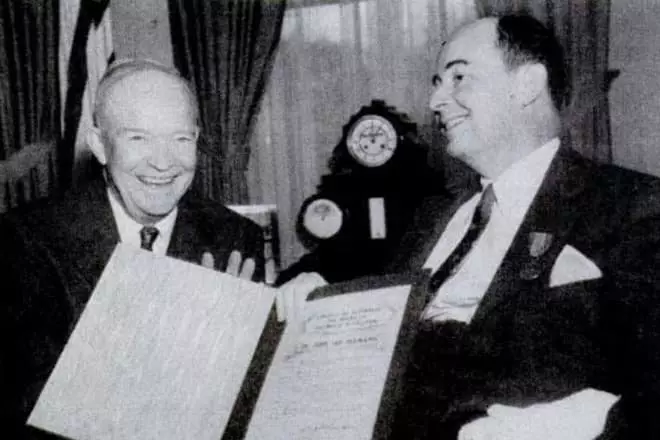

Since the late 1930s, John became the main specialist in mathematics of cumulative charges, advised the Armed Forces of the United States. Being one of the creators of the atomic bomb, the scientist developed the concept and design of explosive lenses used to compress the plutonium nucleus of the weapon, which was soon dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
As a member of the Manhattan Project, von Neumann entered the Committee on the selection of the goals of the atomic bomb and settlements associated with the prediction of the sizes of explosions and the number of dead people. Mathematician, who did not regard this page of the biography as a shameful, became an eyewitty of the first explosive tests at the landfill near the Alamogordo arodrome under the codenate name "Trinity".
In the mid-1940s, John supported the idea of the design of a hydrogen bomb and, together with the theorist Klaus Fuchs, a secret patent filed a secret patent for improving methods and means of using nuclear energy.
In the post-war, von Neumanan made a consultant for assessing the arms system that worked on the government, the military and the CIA. In 1955, the scientist became a UNECE Commissioner and participated in the production of compact hydrogen bombs suitable for transportation on intercontinental ballistic rockets.
Personal life
In 1930, John accepted Catholicism and took his wife a girl named Marietta Köweshi, who studied the economy in the University of Budapest. In 1935, the pair had a daughter Marina, who became a professor of business administration and state policy in Michigan. During visits to Motherland, the von Neumann was carried away by Clara Dan, which soon took the central place in the personal life of mathematics and in 1938 became his 2nd wife.
The new family moved to Princeton and settled in a chic estate, located near the Primary School of Community Park, becoming the center of the Academic Society for the University Town.
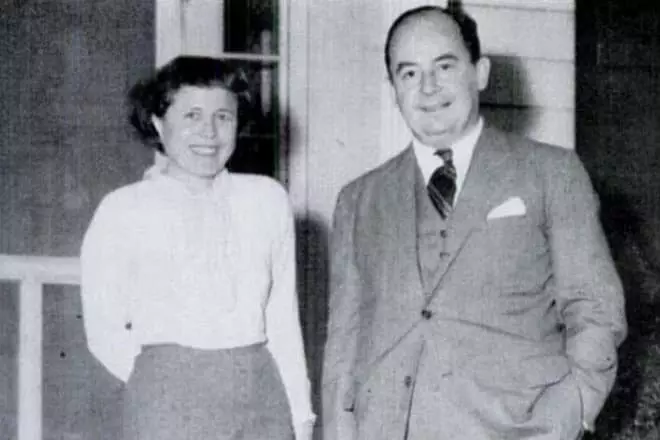

The scientist lived on a wide leg, paying close attention to appearance and home environment, loved delicious food and expensive drinks. Interesting the fact that, working at home, von Neumann turned on the TV at full volume and interfered with the surrounding. Albert Einstein neighbor regularly complained about the noisy German music, coming from the Cabinet John.
In addition, the mathematician acquired a reputation as a bad driver who allowed himself to read the book while driving the car. This provoked several accidents and endless proceedings with the road police.
Death
Health problems at Nimanana began in 1954, when the doctors discovered bone cancer. The real causes of the disease are unknown, but biographers suggest that the tumor could cause irradiation obtained during the work on an atomic project during the Second World War.

The last years and months of life of the Hungarian mathematics passed in the torment related to the recurrences of the disease. In winter, 1957, the physical condition of Neumanan demanded urgent hospitalization, but the treatment did not help, and on February 8, the scientist died at the Walter Reed Medical Center. The cause of death was a malignant tumor of bone tissue.
