Biography
The campaign on the invasion of the Eisenhuer's occupied Nazis was headed by Europe, holding the position of Commander-in-Chief for the European Continent. Norman operation, starting with the sunrise on June 6, 1944, brought success to General. In 1952, representatives of the Republican Party convinced Eisenhower, who at that time commanded the Nasthalnaya Alliance waxes, to participate in the presidential election. Dwight won the number of votes Adlay Stevenson - Democrat, and then re-elected for the second term (1953-1961).
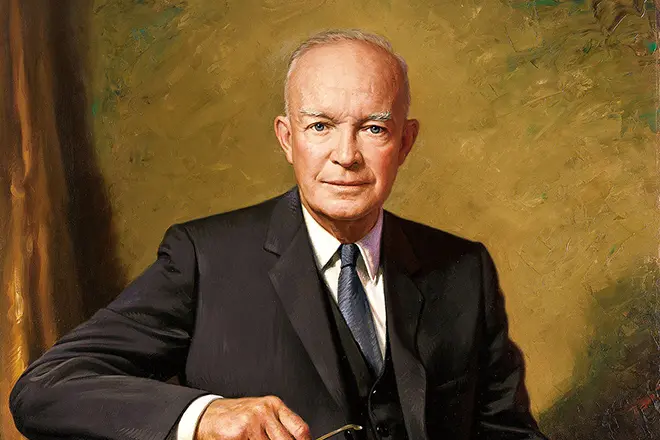

During the reign of Eisenhower, in the context of the real threat to the use of atomic weapons, a fragile relationship with the USSR, completed the war with Korea and sanctioned a number of secret international CIA operations aimed against the communist regime.
In the homeland, in the States, the people enjoyed well-being, and Eisenhuer introduced social programs, created a system of automotive highways and maneuvered behind the scenes in order to discredit Senator Joseph McCarthy, expressed anti-communist glances. The president, although he had public recognition, but slipped on the protection of the rights of Americans of African origin, failed to fully fulfill the mandate of the Supreme Court to merge schools (1954).
Childhood and youth
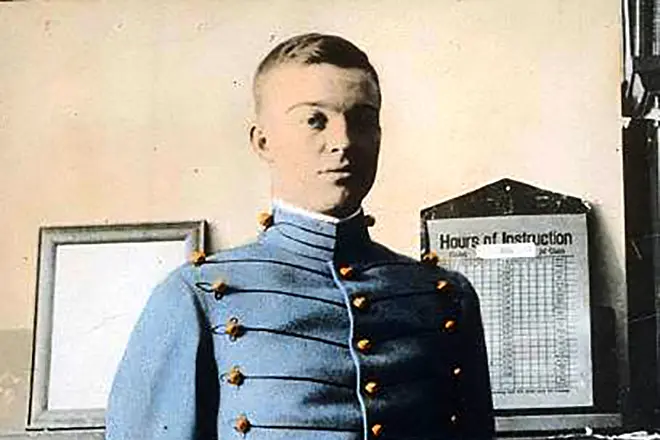
Eisenhuer Dwight was born in Denisone (Texas) on October 14, 1890. The boy has grown in the poor family, where from the seven sons became the third, in the city of Abilen, Kansas. On the parents of the young men biography silent. To the horror of the mother, the pious protestant and pacifirski, the young Ike (as his own closest) became a student of the New York Military Academy in West-Point.
The young man planned to go to Europe, but the end of hostilities was the reason for the disappointment of a young officer. But soon he managed to sign up to the College's team headquarters in Fort Lavenworth (Kansas), as an Assistant John Perrisha, who led the American troops during the First World War, and then Douglas MacArthur, the commander of the US Army headquarters. For four years, Eisenhower lived in the Philippine Islands.
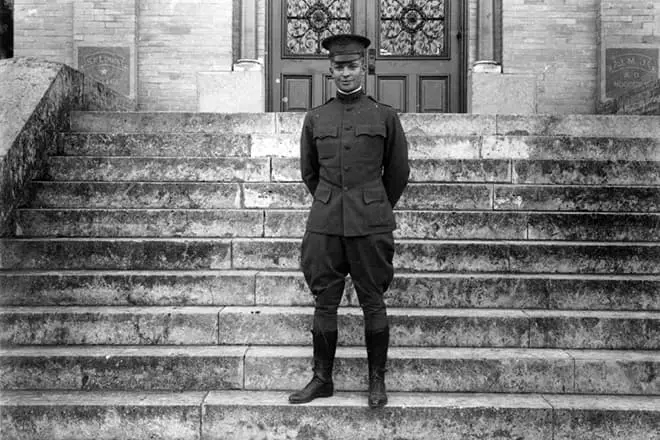
Duight returned to his homeland shortly after the attack of Nazi Germany to Poland, which caused a surge in World War II on the European part of the mainland. Eisenhower headed the Torch campaign in the fall of 1942, and also introduced troops to the countries of North Africa, and then on Sicily Island and mainland Italy, which led to the fall of Rome in the summer of 1944.

In 1943, Eisenhower, who had the rank of Colonel-General, was appointed commander-in-chief, and in December of the same year he initiated the invasion of the troops in the European Essentials. At sunrise on June 6, 1944, the Allies crossed the shed between Great Britain and France and stormed the beaches of Normandy. The result of the invasion was the liberation of Paris on August 25, which decided the outcome of war in Europe. Having risen from the lieutenant colonel to the Supreme Commander in five years, Eisenhower returned to the Hero in the US in order to serve as the headquarters of the US Army headquarters.
Political career
In 1948, Duight left military service and took the position of President of Columbia University. A brief return to the civil lifestyle in 1950 ended when President Harry Truman asked Eisenhuer to take over the command of NATO's new troops on the European continent. In this position, Eisenhuer planned to create a single military organization that could deal with the potential aggression of communists around the world.
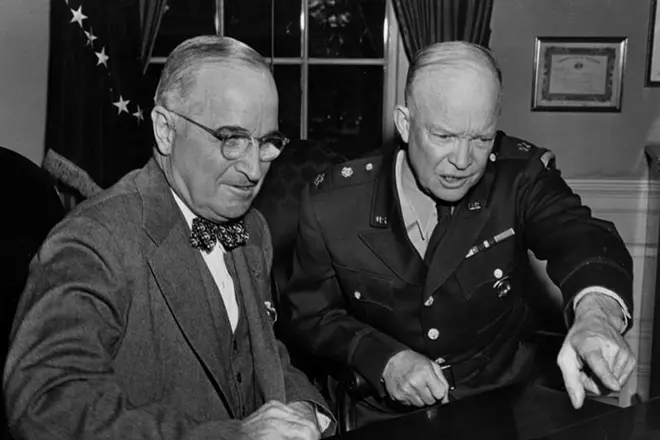

In 1952, when the popularity of Truman fell due to the continuing war with Korea, Eisenhuer under the pressure of Republicans ran for the presidency.
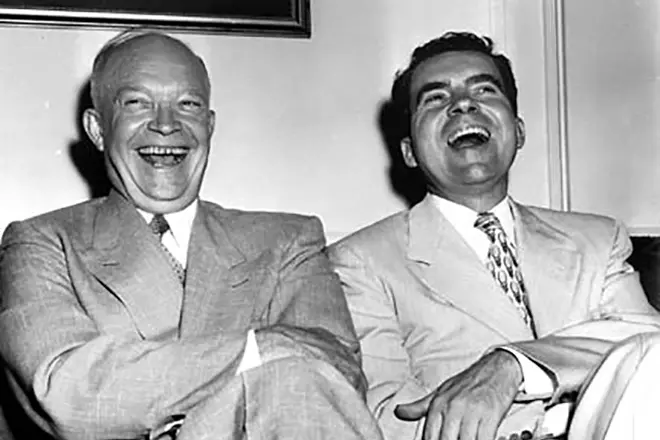

At the national party meeting in July, Dwight by voting is nominated for the first stage of elections. Under the slogan "I like IK", as an assistant to Californian Richard Nikson, Eisenhower defeated Adlay Stevenson to become president of the United States (and re-won the Stevenson after four years, as a result of which he was elected for a second term, despite the health problems after transferred heart attack).
President of the U.S.A
The years of the Board of Eisenhower (01/20/1953-20.01.1961) are characterized by the end of the military mission in Korea, warm relationship with Russia and the beginning of the American Policy "Management of the Peace".
The main directions of the work of Eisenhower:
- Completion of persecution for the manifestation of left views (especially in relation to McCarthy);
- Construction of road highways across the country;
- Growth of the monopoly of the state in the economy;
- "Doctrine Eisenhuer", which staining that every state should count on the aid of the US Army in the event of an attack of other countries.
Although the relationship between the United States and Russia remained relatively warm, including a meeting with Nikita Khrushchev, held in 1959, the shooting of the USSR on the American aircraft "U-2" in the spring of 1960 destroyed the Hope of Eisenhower on the world.
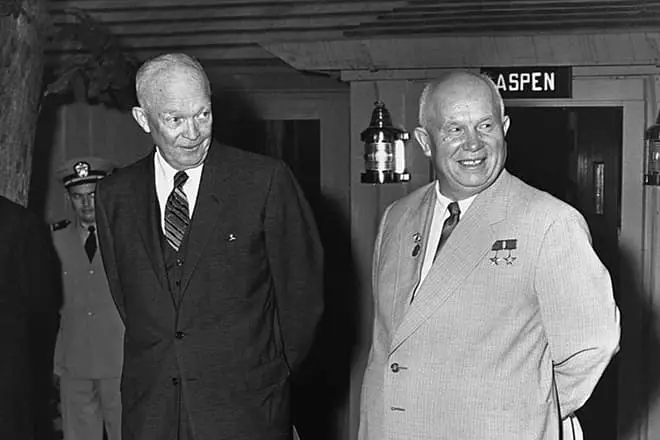

In his farewell speech in the winter of 1961, Eisenhuer spoke about the dangers of the military-industrial complex. As a result of the combination of the defense sector needs with achievements in the field of technologies, the ex-president warned about partnership between the military complex and business, which threatened to have an unjustified influence on the course of international politics. However, warnings were not heard, despite the era of the Cold War.
Domestic politics
Despite the democratic majority in Congress for six of the eight years of his stay at the post, Eisenhower (moderate Republican) achieved numerous legislative victories. In addition to continuing the programs of the New Course and the "fair deal" of his predecessors (Franklin Roosevelt and Truman, respectively), he strengthened social programs, raised the minimum wage level and created the Department of Health, Education and Social Security. In 1956, Eisenhower created an interstate motorway system, built 41,000 miles of roads around the country.
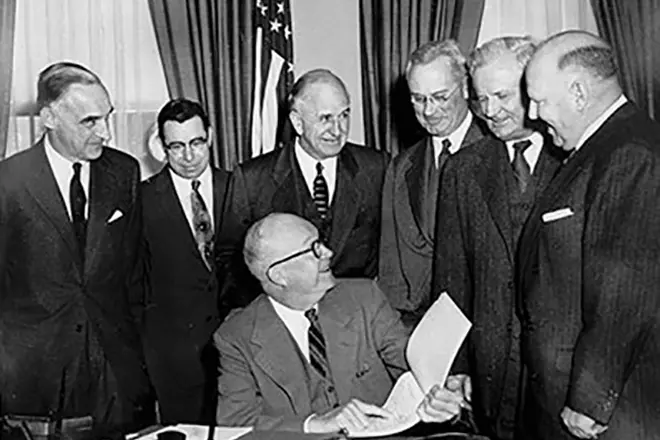

During the first term of Eisenhuer, the anti-communist policy of Senator-Republican Joseph McCarthy violated civil liberties of citizens, which led to a series of sensational television statements in the spring of 1954. To preserve the unity of the party, Eisenhower refrained from the public criticism of McCarthy, although he did not like the senator as a person, but he worked behind the scenes to reduce the influence of McCarthy and ultimately discredit the Republican.

However, Eisenhuer is still incrsigating in the matter of civil rights for African Americans. In 1954, in the case of Oliver Brown, the US Supreme Court decided that the school segregation is unconstitutional. According to Eisenhower, the degrees must occur slowly, and he reluctantly used the presidential power to support the execution of the court sentence, although he sent federal troops to Little Rock, Arkansas, in 1957 to ensure merging of high school there. Eisenhower signed a law on civil rights in 1957 and 1960, providing the federal protection of black voters - the first such law adopted in the United States after the renovation of the South.
Foreign policy
Shortly after the inauguration, Eisenhower signed a truce that became the end of the Korean War. In addition to sending troops to Lebanon in 1958, the armed forces were no longer applied outside the territory of the United States, although the president, without hesitation, sanctioned the spending spending. He authorized the CIA to carry out secret operations against communism in foreign countries, two of which overthrew the rulers of Iran and Guatemala in 1953-1954. In 1954, Eisenhower decided to prevent an air strike on the salvation of France's troops from defeat to Dieen-Bien-Fu, avoiding war at the Indochinese Peninsula, although such support for the Government of the South Vietnam, which had an anti-communist regime provoked the participation of states in the Vietnamese War.

Eisenhuer tried to improve relations with the Soviet Union, especially in 1953, after the death of Joseph Stalin. In the summer of 1955, at a meeting with world leaders in Geneva (Switzerland), he suggested a "open sky" policy, in which the United States and the Soviet Union will conduct cross-checks of military programs in the air. The USSR rejected the proposal, despite its international approval. Under the growing threat of the Soviet technology of nuclear weapons, Eisenhower and John Foster Dulles, who held the post of Secretary of State, achieved success in strengthening the North Atlantic Alliance and the establishment of the Organization of the South-East Agreement, to combat the Communist expansion in the region.
Personal life
Having received a higher education, Eisenhuer in San Antonio met Maymi Geneva Dud, which made a proposal on February 14, 1916. After the wedding, the couple gave birth to two sons - Dudait Duda (who deceased from Scarletin in three years) and John.

The granddaughter Duight Susan entered into marriage with the Russian scientist, symbolicly continued the period of the warm relationship of his grandfather with the USSR government, and grandson married President Nixon's daughter.
Death Dwight Eisenhower
Eisenhuer had consistently high ratings among voters who could not affect the criticism of his regime. Coming out of the office in the winter of 1961, he left for a country house in Gettisburg, where he worked, mainly above the book of memories. President of the USA died on March 28, 1969, after a long disease.Quotes
- "The diplomat is a person who pays a lot to think for a long time before saying nothing."
- "The slogan of true democracy is not" let it make the government, "and" let us do it yourself "
- "We will achieve the world, even if we have to fight for this."
- "What we call foreign affairs are not more than any. It is now internal affairs ... "
Memory
- It is little known that in Potsdam, in 1945, Eisenhuer opposed the use of atomic weapons against Hiroshima and Nagasaki cities. He argued that Japan was already on the threshold of surrender, and the first one who uses such a dangerous new weapon, may damage the prestige of the United States in the international arena, which barely reached its highest point.
- During the meeting of Eisenhower with Zhukov, American treated Marshal "Koloy". Zhukov liked the taste so much that he asked Eisenhuer about the supply of drink exclusively for the headquarters of Zhukov, but the drink should be discouraged. Employees of the plant fulfilled the request of the Russian Marshal and sent 50 beverage boxes to Moscow.

- The opening of the second front brought Eisenhauer the Order of Victory.
- On the role of the United States in the events of World War II, Eisenhower wrote a book called "Crusade in Europe".
- In memory of the 34th US president, Dwight's profile carved on a coin with a nominal one dollar, a portrait on the postage stamps of Kyrgyzstan and the USA.
