Biography
Galileo Galilee is the greatest thinker of the Renaissance era, the founder of modern mechanics, physics and astronomy, follower of the ideas of Copernicus, the predecessor of Newton.
The future scientist was born in Italy, the city of Pisa February 15, 1564. Father Vincenzo Galilee, who belonged to the impoverished genus of the aristocrats, played lute and wrote treatises on the theory of music. Vincenzo was part of the society of Florentine Camerats, whose participants were striving to revive the ancient Greek tragedy. The result of the activities of musicians, poets and singers was the creation at the turn of the XVI-XVII centuries of a new opera genre.

Mother Julia Ammannati led a household and raised four children: Senior Galileo, Virginia, Libya and Michelangelo. The younger son went in the footsteps of the Father and subsequently became famous for composer art. When Galileo was 8 years old, the family moved to the capital Tuscany, the city of Florence, where the Medici dynasty flourished, known for its patronage of artists, musicians, poets and scientists.
At an early age, Galilean was given to school at the Bennedkintse Monastery of Vallomboz. The boy showed abilities for drawing, learning languages and accurate sciences. From Father Galileo inherited the musical hearing and the ability to the composition, but only the science attracted the young man.
Studies
At 17, Galileo goes to Pisa to explore Medicine at the University. The young man, in addition to the main items and medical practice, became interested in visiting mathematical classes. A young man discovered the world of geometry and algebraic formulas, which influenced the worldview of Galilea. For those three years that the young man studied at the university, he thoroughly studied the work of the ancient Greek thinkers and scientists, and also met with the Heliocentric theory of Copernicus.

After a three-year term of stay in the school, Galilee was forced to return to Florence due to the lack of funds for further training from the parents. The leadership of the university did not go for concessions to the talented young man, did not allow the opportunity to finish the course and get a degree degree. But Galileo has already had an influential patron, Marquis Gwidobaldo del Monte, who admired Galilean's talents in the field of invention. The aristocrat patted for the ward before the Tuscan Duchoga Ferdinand I Medici and provided the young man with a salary at the yard of the ruler.
Work at the University
Marquis del Monte helped a talented scientist to get a teacher's place in Bologna University. In addition to lectures, Galileo leads fruitful scientific activities. The scientist is engaged in issues of mechanics and mathematics. In 1689, for three years, the thinker returns to the Pisa University, but now as a teacher of mathematics. In 1692, 18 years old moves to the Venice Republic, the city is Padu.
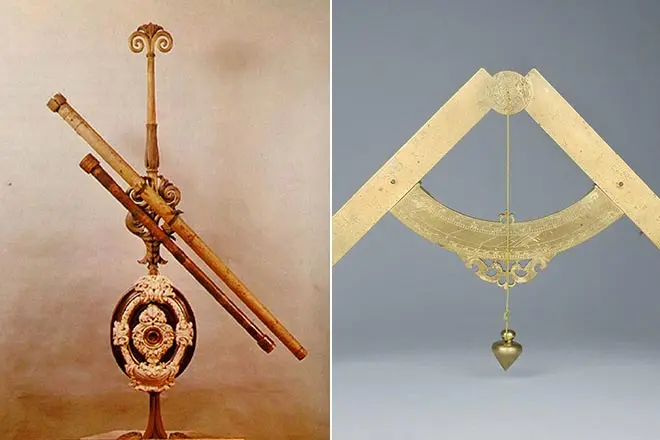
Combining teaching work at the local university with scientific experiences, Galileo publishes books "On Motion", "Mechanics", where he refutes the ideas of Aristotle. At the same years, one of the important events occurs - the scientist is inventing a telescope that has allowed to observe the life of heavenly shining. The discoveries made by Galileem with the help of a new device, an astronomer described in the treatise "Star Bulletin".

Returning in 1610 in Florence, on the care of the Tuscan Duke Kozimo Medici II, Galilee issues an essay of the "sunny spots letters", which was critically met by the Catholic Church. At the beginning of the XVII century, the inquisition acted with a big sweep. And the followers of Copernicus were at the jeques of Christian faith on a special account.
In 1600, Jordan Bruno was executed on the fire, which did not bother his own views. Therefore, the works of Galileo Galilee Catholics were considered provocative. The scientist himself considered himself an approximate Catholic and did not see the contradiction between his works and the Christcentric picture of the world. The Bible astronomer and mathematician considered the book that promotes the salvation of the soul, and not at all the scientific cognitive treatise.
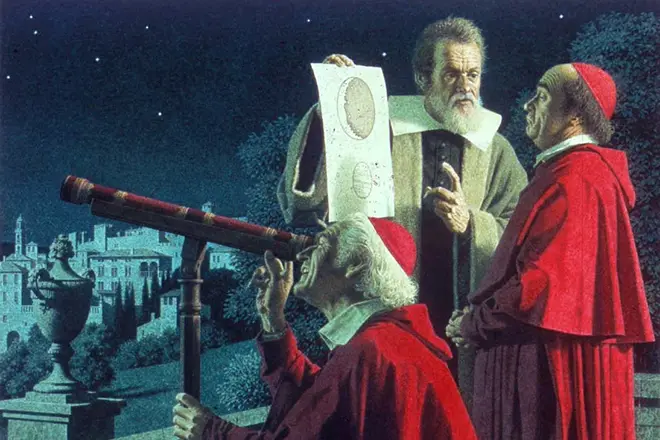

In 1611, Galilee goes to Rome to demonstrate a telescope Pope Paul V. The presentation of the device the scientist spent the most correctly and even received the approval of the capital astronomers. But the request of the scientist to endure the final decision on the problem of the heliocentric system of the world decided his fate in the eyes of the Catholic Church. The papists declared Galilee with the heretic, the accusing process was launched in 1615. The concept of heliocentrism is officially recognized as a false Roman Commission in 1616.
Philosophy
The main postulate of the worldview of Galilee is the recognition of the objectivity of the world, regardless of the subjective perception by man. The Universe is eternal and infinite, initiated by the Divine Pellench. Nothing in space disappears without a trace, only a change in the shape of matter occurs. The material world is based on the mechanical movement of particles, having studied which can be learned by the laws of the Universe. Therefore, scientific activities should be based on the experience and sensual knowledge of the world. Nature on Galileo is a true subject of philosophy, comprehending which you can approach the truth and the primary justice of everything.

Galilee was a commitment of two methods of natural science - experimental and deductive. With the help of the first method, the scientist schoked evidence hypotheses, the second assumed a consistent movement from one experience to another, to achieve complete knowledge. In the work, the thinker relying primarily on the teachings of Archimedes. Criticizing the appeal of Aristotle, Galilee did not reject the analytical method used by the philosopher of antiquity.
Astronomy
Due to the invented in 1609, the telescope that was created using a convex lens and concave eyepiece, Galiley began monitoring the heavenly luminais. But a threefold increase in the first device lacked a scientist for full-fledged experiments, and soon an astronomer creates a telescope with a 32-fold increase in objects.

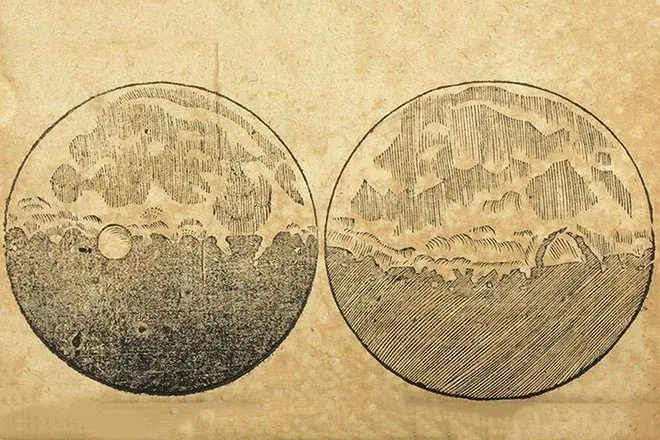
The first luminaire, which Galilee studied in detail with the help of a new device, was the moon. The scientist discovered many mountains and craters on the surface of the Earth's satellite. The first discovery confirmed that the land in physical properties is no different from other celestial bodies. This was the first refutation of Aristotle's approval about the difference in earth and heavenly nature.

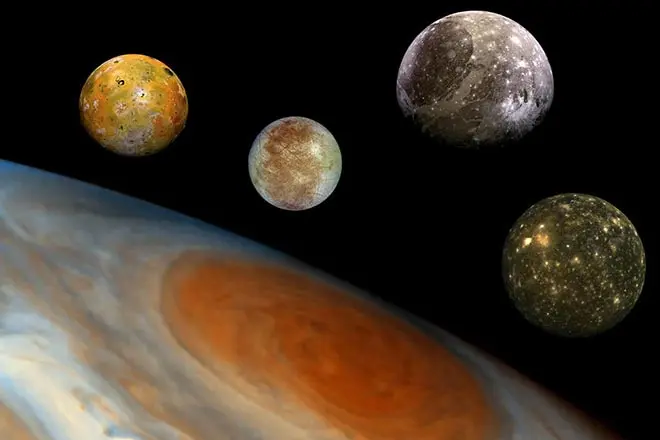
The second major discovery in the area of astronomy concerned the detection of four satellites of Jupiter, which in the 20th century has already been confirmed by numerous cosmic photos. Thus, he denied the arguments of the opponents of Copernicus that, if the moon rotates around the Earth, the land cannot rotate around the sun. Galilee due to the imperfection of the first telescopes could not establish a period of revolutions of these satellites. The final proof of the rotation of the Moon of Jupiter was put forward after 70 years as Astronomer Cassini.

Galileo discovered the presence of solar spots, which he observed for a long time. Having studied the shine, Galiley made the conclusion about the rotation of the Sun around his own axis. Watching the Venus and Mercury, an astronomer determined that the orbits planets are closer to the sun. Galilee discovered the rings of Saturn and even described the planet Neptune, but until the end in these discoveries he failed to advance, due to the imperfection of technology. Watching a telescope behind the stars of the Milky Way, the scientist made sure their immense quantity.
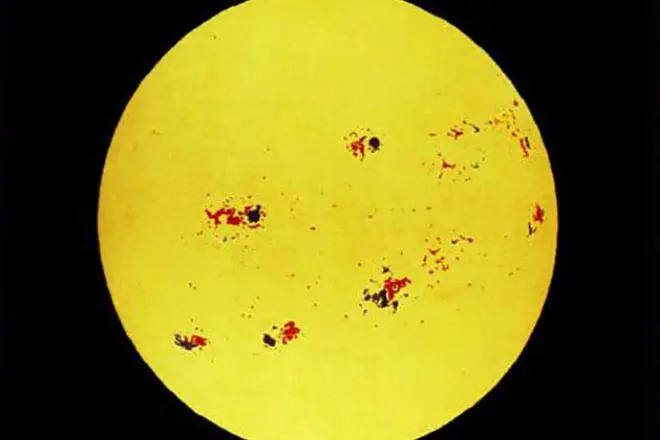
Experimental and empirically, Galile proves that the Earth rotates not only around the Sun, but also around its axis, which further strengthened the astronomer in the correctness of Copernicus hypothesis. In Rome, after the rendered hospitable reception in the Vatican, Galilee becomes a member of the Academy of Dei Linch, which was founded by Prince of Cese.
Mechanics
The basis of the physical process in nature according to Galilee is a mechanical movement. The universe scientist considered as a complex mechanism consisting of the simplest reasons. Therefore, the mechanics became the cornerstone in the scientific activity of Galilee. Galileo made many discoveries in the region directly mechanics, and also identified the directions of future discoveries in physics.
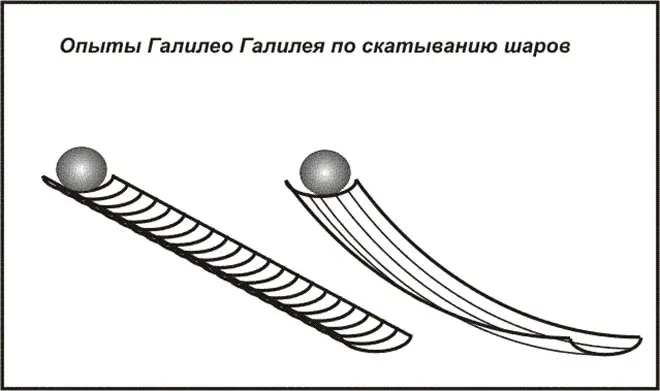
The scientist first established the law of the fall and confirmed it empirically. Galileo opened the physical formula of the body flying, moving at an angle to the horizontal surface. The parabolic movement of an abandoned object was important for calculating artillery tables.
Galiley formulated the law of inertia, which became the fundamental axiom of mechanics. Another discovery was the rationale for the principle of relativity for classical mechanics, as well as the calculation of the formula of the pendulum oscillations. Based on the last study, the first hours with a pendulum in 1657 by Geugenes physicome were invented.
Galilee first drew attention to the resistance of the material than the impetus to the development of independent science. The reasoning of the scientist was subsequently the basis of the laws of physics on the preservation of energy in the field of gravity, the moment of force.
Mathematics
Galilers in mathematical judgments approached the idea of probability theory. Own research on this science, the scientist outlined in the treatise "reasoning about the game in the bone", which was published 76 years after the author's death. Galilee became the author of the famous mathematical paradox on natural numbers and their squares. Galile's calculations recorded in the work "conversations about two new sciences". The developments formed the basis of the theory of sets and their classification.Conflict with church
After 1616, a turning point in the scientific biography of Galilea, he was forced to go into the shadow. The scientist feared to express his own ideas clearly, so the only book of Galileo published after the announcement of Copernicus heretic was the composition of 1623 "Probreshchik." After changing the power in the Vatican Galilee, he took the spirit, he believed that the new dad urban VIII would be favorable to Copernikovsky ideas than his predecessor.
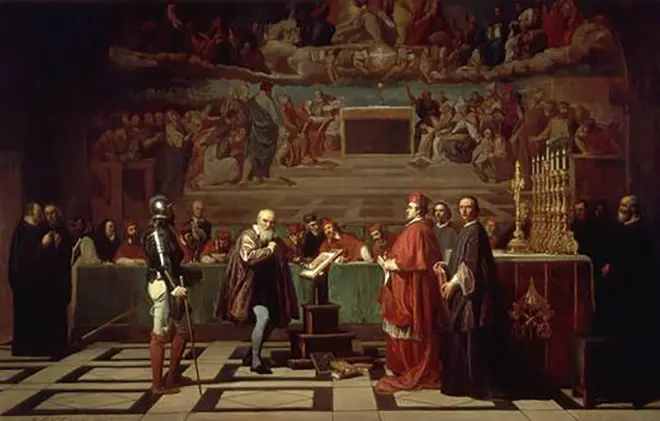

But after the appearance in the press in 1632, the controversial treatise "Dialogue about the two main systems of the world", the Inquisition reappeared against the scientist. The story was repeated with the accusation, but this time for Galileo everything ended much worse.
Personal life
Living in Padua, young Gallile met with the subjects of the Venetian Republic of Marina Gamba, which became the civil wife of the scientist. In the family of Galilee, three children were born - the son of Vincenzo and the daughter of Virginia and Libya. Since the children appeared outside the wedding marriage, the girls subsequently had to become nuns. In 55, Galileo managed to legalize only the Son, so the young man was able to marry and give the father of the grandson, who in the future just as a aunt became a monk.

After the Inquisition declared Galileo out of law, he moved to the villa in Archeryry, which was not far from the monastery of daughters. Therefore, quite often, Galilei could see the favorite, the older daughter Virginia, up to her death in 1634. The younger Libya did not visit her father because of pain.
Death
As a result of short-term imprisonment in 1633, Galilee renounced the idea of heliocentrism and fell under a permanent arrest. The scientist placed under house security in the city of Archeryry with a restriction of communication. Galileo stayed at the Tuscan villa to be easily until the last days of life. The heart of the genius stopped on January 8, 1642. At the time of death, there were two students - Viviani and Torricelli near the scholars. In the 30s, the last works of the thinker were made - "dialogues" and "conversations and mathematical evidence concerning two new industries" in the Protestant Holland.
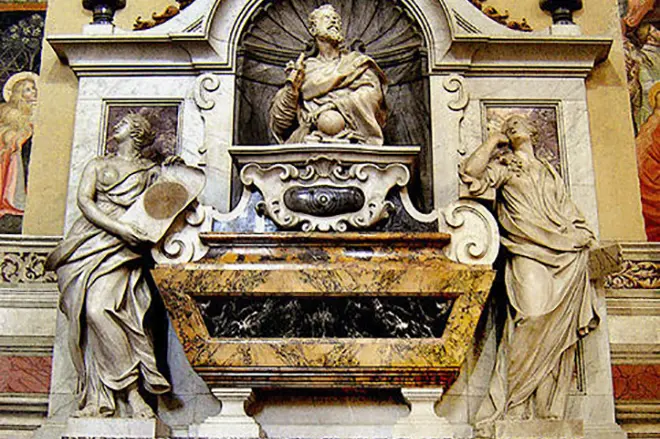

After the death of Catholics were forbidden to bury the dust Galileo in the Santa Croce Basilica crypt, where the scientist wanted to be stubborn. Justice tried in 1737. From now on, Galilee's grave is located next to Michelangelo. After another 20 years, the church rehabilitated the idea of heliocentrism. Galileo's justification had to wait much longer. The mistake of the Inquisition was recognized only in 1992 by the Pope John Paul II.
