Biography
In February 1600, on the square of flowers, Rome was sentenced to death inquisition through the burning of the Italian thinker Jordan Bruno. The personality of Bruno is so ambiguous that about his role in world science and philosophy argue so far. Jordano developed Copernicus theory about the structure of the Universe, assuring that the stars are moving celestial bodies, and the universe is infinite in time and space. But even Galilee with his heliocentric picture of the world, the Inquisition punished only arrest. Why burned Bruno?
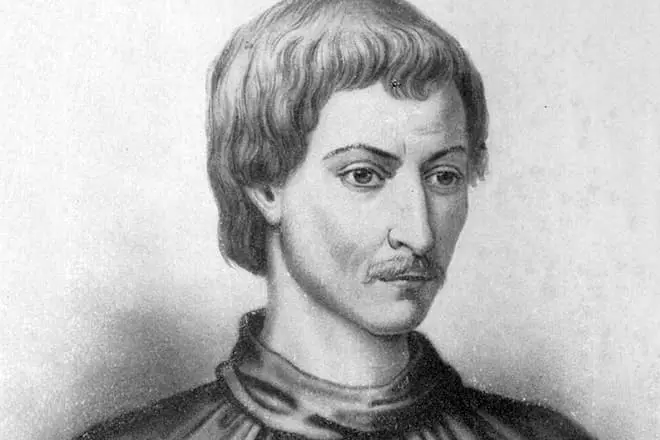

The situation is also interesting because over the past few decades, the Catholic Church has revised a number of decisions of the Inquisition regarding scientists and philosophers, but Jordan Bruno did not enter their number. Moreover, the church supports the decision of the Inquisition. So why did Jordan's servants of the church be unreleased? Was the case in his scientific views or the reason lies much deeper?
Childhood and youth
Philip Bruno was born in 1548, in the town of Nola, near Naples, in the family of a hired soldier Giovanni and a poor peasant. In 1559, the boy went to Naples to learn from sciences, including dialectics, literature and logic. Four years later, Philip sent to the monastery, where he spent 10 years. There, the boy received the second name, under which he became known to the world - Jordano.
At the monastery, Philip studied the book of Copernicus "On the rotation of the heavenly spheres" and opposed the traditional beliefs of Aristotle and Ptolemy, indicating their inconsistency with these practical observations. In 24, Jordano became a priest and spent the first service. Based on the brave statements of the young brother Jordano, the clergymen suspected him in the heresy.

It forced a young monk to go to run. He left the territory of Italy in 1574 and wandered over the territory of Europe. Over the years, Bruno visited Switzerland, England, France, Germany. In 1577, arriving in Toulouse (France), Bruno read lectures on the science and philosophy of Aristotle. Two years later, Jordano, already in Paris, told the public about the works of the philosopher, Thewog Lully, whose worldview was shared and he himself.
But five years later, a conflict with supporters of Aristotle's teachings and he forced to leave Paris, having left Paris, who had come to leave Paris to London. In England, Jordano worked fruitfully and wrote a number of philosophical treatises. In 1586, the thinker went to Germany, but he was banned by lectures in Marburg. Then Bruno took up teaching in Wittenberg.
The science
Jordano Bruno wrote philosophical treatises, spoke on disputes, lectured, but everywhere eventually forced him to stop promoting their ideas. Sanovnik, who later participated in making a death sentence, wrote that Jordano is an outstanding mind, philosopher of outstanding knowledge and readiness.
Bruno resolutely opposed the Catholic Church and in general, against any existing religion at that time, calling them the most serious obstacle to the science to overcome their development. In 1584 his work "On infinity, universe and worlds" was published.
This work is sometimes considered as the basis of modern materialistic environmental studies, including the doctrine of the material unity of the world and the spatial and temporal infinity of the universe.
In the same period, the work "PIR on ash", consisting of five dialogues devoted to the propaganda of astronomical theories of Copernicus. Along with them, the author expresses his ideas about the infinity of the universe and the multiplicity of worlds. In this work, this faith is manifested for the first time as a superman, the Messiah, which is often attributed to the philosopher modern researchers.
Promoting the ideas of Copernicus on the rotation of the Earth and other planets in orbits around the Sun, Bruno did not succeed even from enlightened minds like Bacon and Shakespeare. Disappointed in the states of Central Europe, Bruno went to Prague. There were few more books dedicated to magic.
In general, Bruno's philosophy was based on neoplatonism - he believed that there is a certain start, who gave the continuation of everything in the universe. But not only initially called the thinker by God, and in nature, and even a person - this church is erased and could not.

Today, researchers argue that there were no significant scientific significance of the idea of Bruno, since they only continued the doctrine of Copernicus, expanding it, but not confirming the evidence base. All the main ideas and discoveries of Jordano lay in the plane of mysticism or psychology, and not astronomy at all.
However, to completely deny the value of the discoveries of Bruno for modern science. Incorrectly: the philosopher first put forward the hypothesis about the movement of the continents, the presence of distant planets, invisible person, etc.
Personal life
About personal life Bruno practically nothing is known. Jordano was not married, did not have children, and even the pupils and followers had no thought. Some biographers allow for the assumption of the homosexual inclination of the philosopher. However, it is not surprising for the morals of the Middle Ages and, in particular, for servants of the Church.
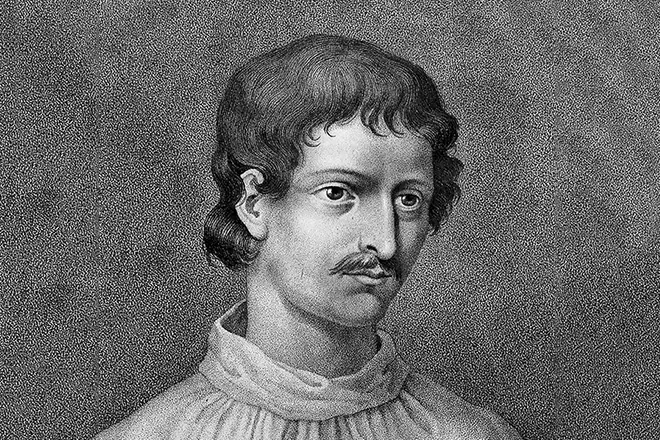

In the photo of the preserved portraits, Jordano appears to a fragile young man with a thoughtful expression. This thoughtfulness, passionateness of science and mystics replaced the man of the delights of secular life and carnal joy in the arms of women.
Death
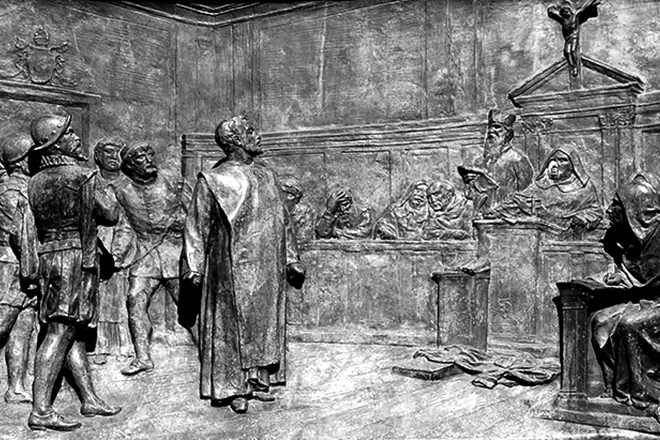
Returning from the wanderings in Europe back to Italy, Jordan Bruno immediately fell into the hands of the Inquisition. According to a number of biographers, the philosopher could avoid a death sentence, if it were not for his performances against monastic profits and estates and not the requirements for their confiscation. Other researchers believe that the statements of the thinker about the multiplicity of worlds and the infinity of the universe became the main reason that caused the anger of the Inquisition.
But after all, the Galilean's theories clearly contradicted church doctrines, why did the Inquisition treat him much softer and tolerate? According to the researchers, the answer to this question lies in the methods used by thinkers. Galileo was a classic scientist who used mathematical tools in the development of theories. And Jordano, rather, a mystic, a thinker, who used magic instead of scientific methods where there was not enough arguments.
A number of biographers say that the execution of Jordan Bruno became the result not so much to fight with science and enlightenment, how much struggle for power. Bruno was incredibly convincing in his teachings, and his main ideas were to reject religion as such, which was a rather dangerous liberty in the Epoch of the Middle Ages. Bruno arrested after the denunciation of a certain uchenigo, accusing the philosopher in heresy. The trial lasted six years, which the philosopher spent in imprisonment in a Roman prison.
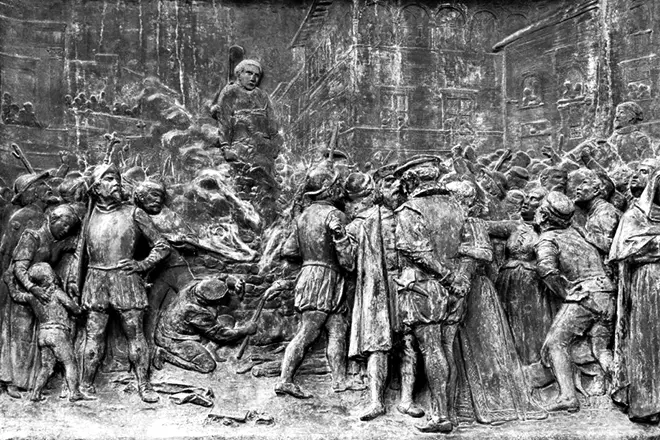

A number of researchers believe that the Inquisition gave the opportunity to the former priest to renounce the heresy and stay alive, but he refused. The text of the sentence, which was carried out inquisition against Jordano, was lost, it is only known that the fault was not at all in scientific theories, but in the blasphemy of the former minister of the Church. It was the threat of church authorities that became the main cause of the executive execution and stubborn philosopher.
Interesting Facts
The personality of Jordano Bruno is so extraordinary that the myths about it walks more than the facts of a real biography. This is due to the ambiguous relationship of researchers to its theories and teachings. And indeed, a number of interesting facts took place in the life of the thinker. So, in the period of life, at the monastery, Brother Jordano expressed doubts about the impassion of the conception of Jesus Christ by Virgin Maria, leading to the horror of the Holy Fathers. This fact then often recalled the Inquisition during the trial.
Long-term work in France, despite the rejection of the church of the philosopher's ideas by local ministers, is explained by phenomenal memory. Herrich III drew attention to it and asked for him to teach him the mnemonics. With the same request later turned to Bruno an aristocrat from Venice, but later the Donos wrote the Donos to his teacher, accusing him in heretical statements.
According to Velmazby, Jordano considered Jesus magician and argued that his death was random, and the sins of mankind did not swim at all, and the human souls were not immortal in the sense, which invests in this concept of Christians, but are subjected to reincarnation after the death of the physical body.

The sentence made as a result of a philosopher sounded like a "executionless blood execution", which meant death at the fire. And the works of Jordano Bruno were in the list of literature prohibited by the Catholic Church, until the middle of the twentieth century.
Now, on the square of flowers in Rome, there is a monument to a thinker who considered himself a martyr. But even the discovery of the monument passed with a scandal and an anticatolic demonstration. Another interesting fact is that, despite the desire of the Church, later, a secular society rehabilitated a philosopher: in 1973, it was even a film with the same name in Italy, and even the crater on the moon wears the name of Jordan Bruno.
Bibliography
- 1582 - "On the shadows of ideas"
- 1582 - "Art of Memory"
- 1582 - "Song of Circeda"
- 1582 - "On the abbreviated construction and supplement of the art of Lully"
- 1583 - "Memorial Art", or "The Art of Remembering"
- 1583 - "Printing seals"
- 1584 - "Pier on ash"
- 1584 - "On the cause, beginning and one"
- 1584 - "On infinity, universe and worlds"
- 1585 - Killensky Donkey
- 1586 - "On the interpretation of dreams"
- 1588 - "Abstracts against mathematicians"
- 1595 - "Code of Metaphysical Terms"
