Biography
René Descartes - mathematician, philosopher, physiologist, mechanic and physicist, whose ideas and discoveries played a big role in the development of several scientific industries at once. He developed an algebraic symbolism, which we use to this day, became the "father" of analytical geometry, laid the foundations for the formation of reflexology, created mechanism in physics - and this is not all achievements.Childhood and youth
Rene Descartes appeared in the city of La on March 31, 1596. Subsequently, the name of this city was renamed Decartes. Rena's parents were representatives of the old nobility, which in the XVI century barely reduced ends with the ends. Rena became the third son in the family. When Descarte was 1 year old, the mother died suddenly. The father of the future famous scientist worked as a judge in another city, therefore rarely visited children. Therefore, after the death of Mother, the grandmother took up the macarten-younger.
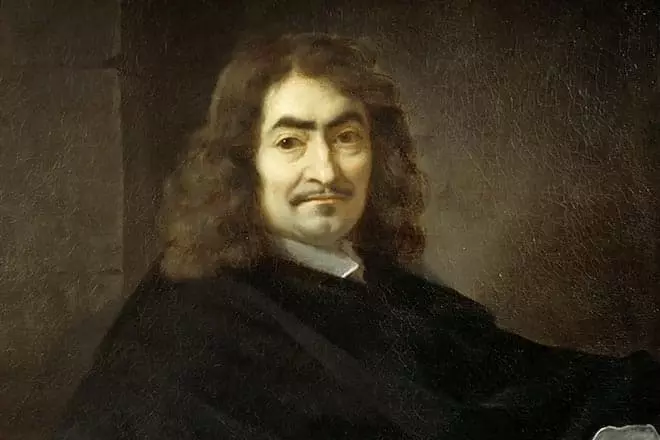

From early years, Rene has demonstrated striking curiosity and desire to gain knowledge. In this case, he had fragile health. The first education boy received in the Jesuit College of La Flash. This educational institution was distinguished by a strict regime, but Descarte, taking into account the state of health, did in this mode of relaxation. For example, he could wake up later than other students.
As in most colleges of that time, in La Flash, education was religious. And although the study meant a lot for the young Descartes, such an orientation of the educational system gave up and strengthened it in him a critical attitude towards the philosophical authorities of that time.

Having completed his studies in the board, René went to Poitiers, where he received a bachelor's degree in law. Then spent some time in the French capital, and in 1617 he entered military service. Mathematics participated in hostilities in the territory of Holland, while the revolution absorbed by the revolution, as well as in a short battle for Prague. In Holland, Decartes made friends with physicist Isaac Bekman.
Then Rena lived for some time in Paris, and when the followers of Jesuit learned about his bold ideas, went back to Holland, where he lived for 20 years. Throughout life, he was persecuted and attacks from the Church for progressive ideas, who had faded the level of development of the science of the XVI-XVII centuries.
Philosophy
The philosophical teaching of René Descartes was peculiar to dualism: he believed that there was an ideal substance, and material. And then, and the other began recognized them with independent. The concept of Rene Descartes also involves the recognition of the presence of two kinds of entities in our world: thinking and extended. The scientist believed that God was the source of both entities. It forms them according to the same laws, creates matter in parallel with its peace and movement, and also retains substances.

A peculiar universal method of knowledge of René Descartes saw in rationalism. At the same time, the knowledge of the scientist considered a prerequisite for the fact that a person will dominate the forces of nature. The possibilities of reason on Descartes are abandoned by the imperfection of a person, its differences from the perfect God. Renee's reasoning about knowing in such a way, in fact, laid the base of rationalism.

The initial point of most searches for Ren Decartes in the field of philosophy was doubtful in the truth, the error of knowledge relating to generally accepted. Captation Descartes "I think - therefore, I exist" due to these arguments. The philosopher stated that each person could doubt the existence of his body and even the outside world as a whole. But at the same time, this doubt remains unambiguously.
Mathematics and physics
The main philosophical and mathematical result of the work of Rene Descartes was the writing of the book "reasoning about the method". The book contained several applications. One application contained an analysis of analytical geometry. Another application included the rules for studying optical instruments and phenomena, achievements of Cartarate in this industry (for the first time correctly compiled the law of refraction of light) and so on.
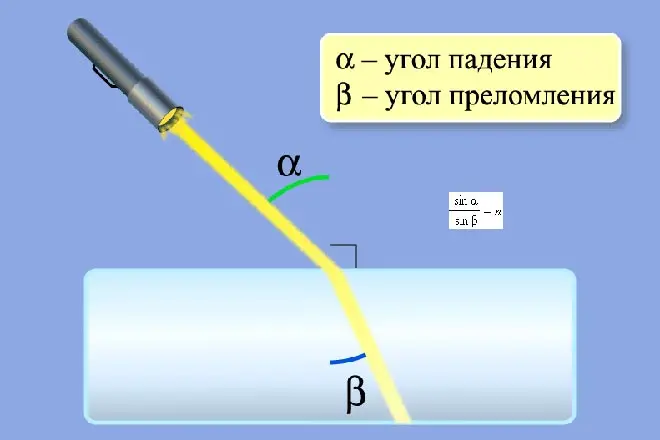
The scientist introduced the degree used now, the line above the expression that was taken under the root began to denote the symbols "X, Y, Z", and permanent values - the characters "A, B, C". The mathematician also developed the canonical form of the equations, which today is used in solving (when zero is in the right part of the equation).
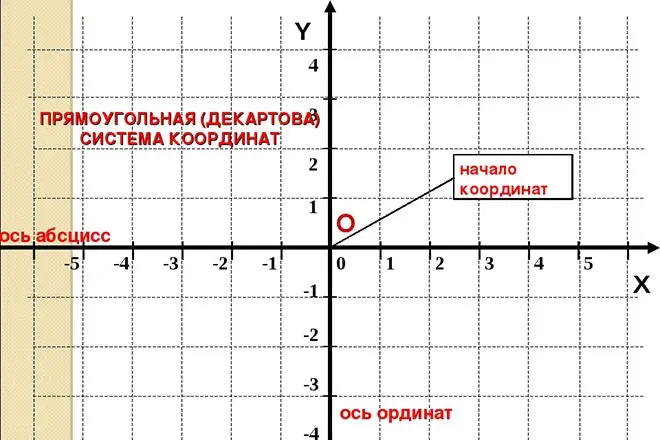
Another achievement of Rene of Descartes, important to improve mathematics and physics, is the development of a coordinate system. The scientist introduced it in order to make it possible to make a description of the geometric properties of bodies and curves in the language of classical algebra. In other words, it was René Descartes who made it possible to analyze the equation of the curve in the Cartesian coordinate system, which is a special occasion of which is a well-known rectangular system. This innovation also allowed much more and more accurate to interpret negative numbers.
The mathematician explored algebraic and "mechanical" functions, while arguing that there is no single method for studying transcendental functions. Descartes preferably studied real numbers, but began to take into account and complex. It introduced the concept of imaginary negative roots conjugate with the concept of complex numbers.
Studies in the field of mathematics, geometry, optics and physics subsequently became the basis of the scientific papers of Euler, Newton and a number of other scientists. All mathematicians of the second half of the XVII century founded their theories on the works of Rene Descartes.
Decorate method
The scientist believed that experience is necessary only to help the mind in those situations when it is impossible to come to truth exclusively. Thirty of all the scientific life of Descartes carried four main components of the truth search method:- It is necessary to start from the most obvious, not subject to doubt. With the opposite of what it is even impossible to allow.
- Any problem should be divided into so many small parts as it takes to achieve its productive solution.
- It should be started with a simple, from which you need to gradually move to more and more complex.
- At each stage, it is necessary to recheck the correctness of the compiled conclusions so that according to the results of the study, to be confident in the objectivity of the knowledge gained.
Researchers note that these rules that Decartes invariably used, creating works, brightly demonstrate the desire of the European culture of the XVII century to the abandonment of obsolete rules and to build a new, progressive and objective science.
Personal life
About the personal life of Rene Descartes knows little. Contemporaries argued that in society he was arrogant and silent, preferred to solitude to companies, but in a circle of loved ones could show amazing activity in communication. Rena's wife, apparently, was not.

In adulthood, he was in love with the maid, who gave him the daughter of Francin. The girl was illegally born, but Decartes loved her very much. At the five-year-old age, Francine died due to scarletna. Her death scientist called the biggest tragedy of his life.
Death
Over the years, Rene Descartes suffered an injury for a fresh look at science. In 1649, he moved to Stockholm, where he was invited by the Swedish Queen of Christina. With the last decartes, many years have rewritten. Christina was defeated by the genius of a scientist and promised him a quiet life in the capital of his state. Alas, life in Stockholm Rene enjoyed for a short time: shortly after the move he was cold. The cold quickly turned into inflammation of the lungs. The scientist went to the world in another February 11, 1650.

There is an opinion that Decartes did not die due to pneumonia, but because of poisoning. In the role of evidence, agents of the Catholic Church could act, which was not the presence of a liberated scientist next to the Queen of Sweden. The last Catholic Church intended to turn into his faith, which happened four years after the death of Rene. An objective confirmation of this version today did not receive, but many researchers are inclined to it.
Quotes
- The main action of all human passions is that they encourage and configure the soul of a person to wish what these passions prepare his body.
- In most disputes you can notice one error: while truth lies between two protected views, each of the latter leaves it, the farther than with a large heat argue.
- An ordinary mortal sympathizes those who are more complaining because he thinks that the mountain of those who complain are very large, while the main reason for the compassion of great people is the weakness of those from whom they hear complaints.
- Philosophy because it applies to all available for human knowledge, one only distinguishes us from savages and barbarians, and every people are the more citizen and educated, the better in it philosophy; Therefore, there is no greater good for the state, how to have true philosophers.
- Curious looks for rarity only then to surprise them; Curious then to learn them and stop surprising.
Bibliography
- Philosophy of Spirit and Matter Rene Descartes
- Rules for the leadership of the mind
- Slaving truth through natural light
- World, or the light treatise
- Reasoning about the method to correctly send your mind and find the truth in the sciences
- Initially, philosophy
- Description of the human body. On the formation of an animal
- Remarks on a certain program published in Belgium at the end of 1647 under the title: Explanation of the human mind, or a reasonable soul, where it is explained that it represents and what can be
- Passion soul
- Reflections on the first philosophy, in which the existence of God and the distinction between the human soul and the body are proved in
- The objections of some scientists against the above "reflections" with the answers of the author
- Deep to Father Dina, the provincial abbot of France
- Conversation with Burner
- Geometry
- Cosmogony: two treatises
- Initially, philosophy
- Reflections on the first philosophy
