Biography
"As long as people enjoy electricity benefits, they will always remember the name of Faraday," said German Helmgolts.Michael Faraday is an English physicist experimenter, a chemist, the creator of the exercise on an electromagnetic field. It opened electromagnetic induction, which is the basis of industrial production of electricity and applications in modern conditions.Childhood and youth
Michael Faraday was born on September 22, 1791 in Newington Batts, not far from London. Father - James Faraday (1761-1810), Kuznets. Mom - Margaret (1764-1838). In addition to Michael, Robert and Sisters Elizabeth and Margaret grew in the family. They lived poorly, so Michael did not reassure himself at school and went to work in a bookstore at 13 years old.
Education is failed. The reading of books in physics and chemistry was satisfied with the knowledge of the knowledge of the books in the book shop in excess. The young man mastered the first experiments. Built the current source - "Leiden Bank". Father and brother supported Michael in a pull to experiments.
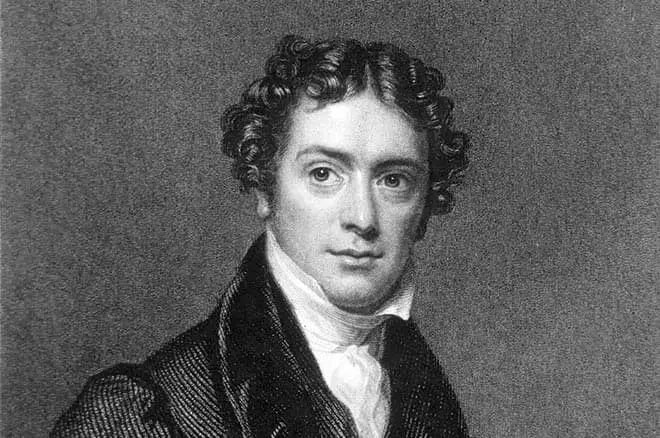

In 1810, the 19th-year-old young man became a member of the philosophical club, in which lectures on physics and astronomy were read. Michael participated in scientific controversy. A gifted young man attracted the attention of the scientist community. Buyer of the bookstore William Dance presented Michael a gift - a ticket to visit a number of lectures in chemistry and physics of Davy Gemphri (the founder of the electrochemistry, the discoverer of the chemical elements of potassium, calcium, sodium, barium, boron).
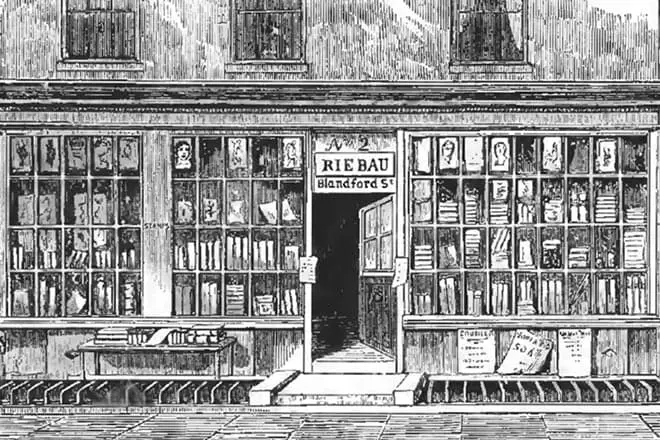

Future scientist, shying the lectures of Gemphri Davy, made a binding and sent a professor, accompanied by a letter to find some work at the Royal Institute. Davy took part in the fate of the young man, and after a while, 22-year-old Faradays received a laboratory work in a chemical laboratory.
The science
Performing the responsibilities of a laboratory assistant, Faradays did not miss the opportunity to listen to lectures, in the preparation of which participated. Also, with the blessing of Professor Davy, a young man conducted his chemical experiments. The conscientiousness and art of the work of the work with a laboratory assistant made it a constant Assistant Davy.
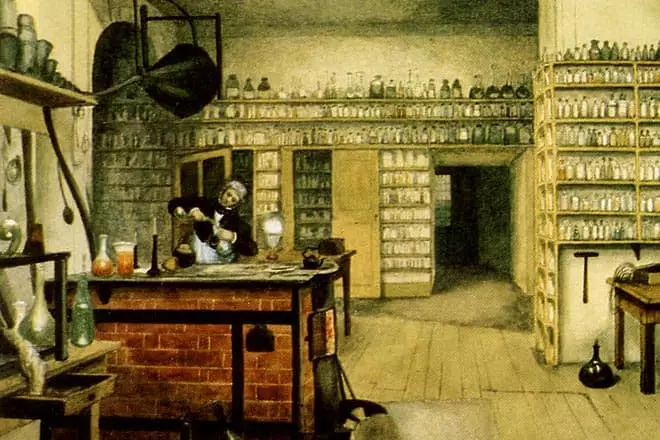

In 1813, Davy took the Faraday secretary in a two-year-old European journey. During the trip, the young scientist met with the luminaries of world science: Andre-Marie Ampera, Joseph Louis Gay-Loussak, Alessandro Volta.
Upon returning to London in 1815, Faraday received the post of assistant. In parallel, the favorite thing continued - put his own experiments. For the life of Faraday, there were 30,000 experiments. In scientific circles for pedantry and hard work, he received the title of "King of Experiments". A description of each experience carefully losted into diaries. Later, in 1931, these diaries were published.
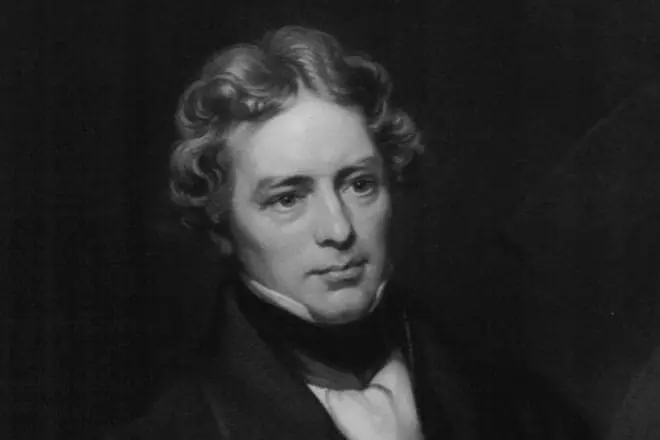

The first print edition of Faraday was published in 1816. By 1819, 40 works were printed. Proceedings are devoted to chemistry. In 1820, from a number of experiments with alloys, a young scientist discovered that the alloy of steel with the addition of nickel does not give oxidation. But the results of the experiments passed by the metallurgists. The opening of stainless steel was patented much later.
In 1820, Faraday became a technical caulier of the Royal Institute. By 1821, he switched to physics from chemistry. Faradays performed as a prevailing scientist, acquired weight in the scientific community. An article was published on the principle of the electric motor, which placed the beginning of industrial electrical engineering.
Electromagnetic field
In 1820, Faraday was carried away by the experiments on the interaction of electricity and the magnetic field. By this time, the concepts of "DC source" (A. Volt), "Electrolysis", "Electric arc", "Electromagnet" discovered. During this period, electrostatics and electrodynamics developed, the experiments of Bio, Savara, Laplace on working with electricity and magnetism were published. A. Ampere on electromagnetism was published.
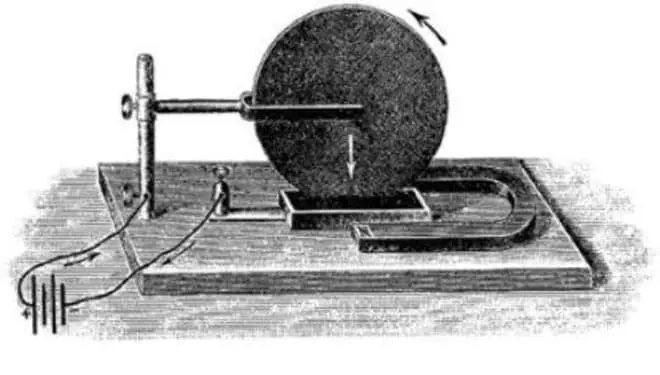
In 1821, the light saw the work of Faraday "On some new electromagnetic movements and about magnetism theory". In it, the scientist presented the experiments with a magnetic arrow rotating around one pole, that is, it carried out the transformation of electrical energy into mechanical. In fact, he introduced the first in the world, albeit a primitive, electric motor.
The joy of discovery spoiled the complaint of William Vollarston (opened palladium, rhodium, constructed a refractometer and a goniometer). In a complaint to Professor Davy, the scientist accused Faraday in the stealing ideas with a rotating magnetic arrow. The story took scandalous. Davy took the position of Vollaston. Only a personal meeting of two scientists and clarifying their position by Faraday was able to settle conflict. Vollarston abandoned the claims. Davy and Faraday relations have lost their former trust. Although the first until the last days was not tired of repeating that Faradays are the main discovery made them.
In January 1824, Faraday was elected by a member of the Royal Society London. Professor Davy voted against.
In 1823 he became a corresponding member of the Paris Academy of Sciences.
In 1825, Michael Faraday took the place of Davi as director of the Laboratory of Physics and the Chemistry of the Royal Institute.
After the discovery of 1821, the scientist did not publish work. In 1831, he became Professor Vuljah (Military Academy), in 1833, a professor at the chemistry of the Royal Institute. He conducted scientific disputes, lectured in scientific meetings.
Back in 1820, Faraday was interested in the experience of Hans Ersteda: the movement along the electric current circuit caused the movement of the magnetic arrow. The electric current caused the occurrence of magnetism. Faraday suggested that, accordingly, magnetism may cause an electric current. The first mention of the theory appeared in the diary of the scientist in 1822. Ten years of experiments went to the raystery of the secrets of electromagnetic induction.
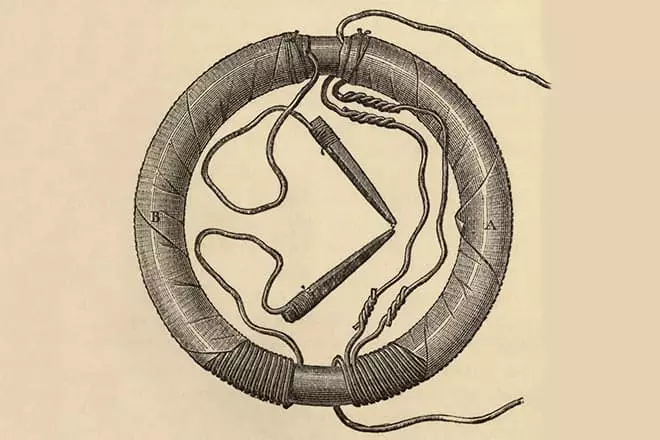
The victory came on August 29, 1831. The device, which allowed the Faraday to make a brilliant discovery, consisted of an iron ring and a set of turns of the wire from copper wound into two half. In the chain of one half of the ring, closed wire, was a magnetic arrow. The second winding connected to the power battery. When the current is turned on, the magnetic arrow made fluctuations in one direction, and when turned off to another. Faraday concluded that the magnet is able to convert magnetism into electrical energy.
The phenomenon "The occurrence of electric current in a closed circuit with a change in the magnetic flux passing through it" was called electromagnetic induction. The detection of electromagnetic induction opened the way the current source of the current - an electric generator.
The discovery marked the beginning of a new fruitful twist of scientist experiments who gave the world "Experimental Research on Electricity". Faradays experienced proved a single nature of the occurrence of electrical energy, independent of the method, with which the electrical current is caused.
In 1832, physics awarded the Copli medal.
Faraday became the author of the first transformer. He belongs to the concept of "dielectric constant". In 1836, by a number of experiments, he proved that the charge of the current has an impact only on the conductor shell, leaving objects inside it intact. In the applied science, the device made on the principle of this phenomenon is called the Faraday Cell.
Discoveries and works
Opening Michael Faraday is devoted not only to physics. In 1824, the benzene and isobutylene opened them. The scientist brought the liquid shape of chlorine, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, ammonia, ethylene, nitrogen dioxide, obtained hexahloran synthesis.

In 1835, Faraday due to the disease was forced to make a two-year break in work. The cause of the disease was suspected of contacting the scientist during experiments with mercury couples. For a short trip after recovery, in 1840, the professor again felt bad. Persected weakness, there was a temporary memory loss. The recovery period was delayed for 4 years. In 1841, at the insistence of doctors, the scientist went on a journey through Europe.
The family lived in almost poverty. According to the testimony of the Biograph Faraday John Tyndal, the scientist received a pension of 22 pounds per year. In 1841, Prime Minister William Lam, Lord Melbourne, under the pressing of the public signed a decree appointing the Faraday of the state pension in the amount of 300 pounds per year.
In 1845, a great scientist managed to attract the attention of the world community with some more discoveries: the discovery of the change in the plane of polarized light in the magnetic field (the "Faraday effect") and diamagnetism (magnetization of the substance to the external magnetic field acting on it).
The Government of England did not once asked Michael Faraday to help solve problems related to technical issues. The scientist developed a program of equipment of lighthouses, the methods of combating corrosion of ships, performed by a judicial expert. Being by nature a man good-natured and peace-loving, flatly refused to participate in the creation of chemical weapons for the war with Russia in the Crimean War.

In 1848, Queen Victoria presented the house on the left bank of the Thames, Hampton Court. The British Queen paid costs and taxes around the house. The scientist with his family moved to him, leaving the case in 1858.
Personal life
Michael Faraday was married to Sara Barnard (1800-1879). Sarah - sister friend Faraday. The proposal of the hand and hearts 20-year-old girl did not immediately - the young scientist had to collapse. A quiet wedding took place on June 12, 1821. Many years later, Faraday wrote:"I married - an event that more than any other contributed to my happiness on earth and my healthy state of the spirit."Faraday family, like family of his wife, members of the Protestant community "Sandemian". Faraday performed the work of the London community's deacon, was repeatedly chosen elder.
Death
Michael Faraday was sick. In short moments, when the disease retreated, he worked. In 1862, he put forward a hypothesis about the movement of spectral lines in a magnetic field. Confirm the theory was able to Peter Zeeman in 1897, for which in 1902 he received the Nobel Prize. Faraday Zeeman called the author of the idea.
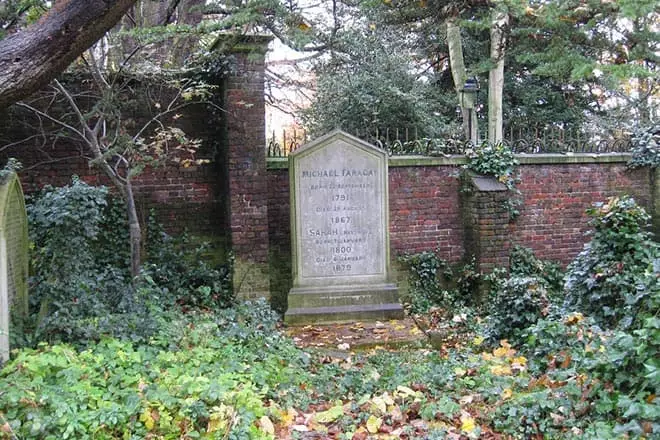

Michael Faraday died at the desktop on August 25, 1867 at the age of 75. He is buried next to his wife at the Highgate Cemetery in London. The scientist asked before his death about a modest funeral, so only relatives came. On the gravestone, the name of the scientist and years of life is carved.
Interesting Facts
- The physicist's scientist did not forget about children. Lectures for children "Candle History" (1961) reprinted to this day.
- The portrait of Faraday is placed on the British bill of 20 pounds of the 1991-1999.
- There were rumors that Davy did not answer Faraday to a request for work. Once, temporarily losing sight during a chemical experiment, Professor remembered the persistent young man. Having worked as secretary of the scientist, the young man so shook Davy with his erudition that he suggested Michael work in the laboratory.
- After returning from the European tour with the family of Davie Faradays, waiting for the assistant's place in the Royal Institute there was a dishwasher there.
