Biography
The founder of genetic science in the USSR, academician, biologist and breeder. The person of the encyclopedic mind, who posted five European languages, in 41 years old became the president of the Academy of Agricultural Sciences.

Nikolai Ivanovich Vavilov was born in 1887 in the family of the Moscow merchant of the Second Guild of Ivan Ilyich Vavilov, a nugget from the peasants. Vavilov managed a shoe manuff, and in 1909 Ivan Ilyich elected a member of the Meeting of the City Duma. The family of the industrialist lived in his own house on medium fores. Mom - Alexander Mikhailovna Postnikova - from the prosperous Moscow family of employees of manufactory.

Three of the seven Wavilov children died in infancy. Nikolai's younger sister - Lydia Vavilov, microbiologist - died from black smallpox in 1914, infected with a deadly disease in the expedition. Sergey Vavilov's younger brother, famous physics and academician, was not in 1951 (died of heart attack).

My father dreamed that sons would go to his footsteps and continued a family business. But the eldest, having laid down herbariums and geographical maps, studied biology textbooks, the younger was carried away by physics and mathematics. Father tried to "convince" offspring with the help of a belt, scolded them, but sons inherited from the head of the family a hard character.
After graduating from the gymnasium, Nikolai and Sergey lost to the father and entered the commercial school on the oozen, but the dreams of a scientific career won. Nikolai, not wanting to spend a year to explore the Latin language needed when entering the Imperial Moscow University, in 1906 he became a student of the agricultural institution, choosing agroset. Sergey entered the Physics and Mathematics Faculty of the Moscow University.

Teachers of Vavilov in the agricultural university were Master Botanist Nikolai Khudyakov and the founder of the agronomic chemistry Dmitry Sanids, shining Soviet agrarian science. Under their start, Nikolay was formed as a scientist.
Selection and genetics
At the Institute, at the initiative of the Academician and Biochemistry, Dmitry Spicynikova Nikolai Vavilov studied the selection. Having received a diploma of the Academy, moved to the St. Petersburg Bureau of Applied Botany.
In 1913, a talented biologist was sent to learn abroad. In the commune Vilmren in France, he got acquainted with breeding seeds, in German Jena and English Merrton worked in laboratories. Six months worked with the famous biologist William Baton. In Cambridge, Nikolai Vavilov continued to explore the bread cereals, driving seed seeds brought from Russia to the university farm.

The scientific campaign broke out due to the World War I began. The invited commission freed the young scientist from the service: Nicholas found a long-standing eye injury.
In 1916, Vavilov visited North Iran, Fergana and Pamire. Traveling has collected a scientific material, developed the laws of homologous series and established the focus of the spread of cultivated plants.
The revolutionary events of 1917, stunned Russia, found Nikolai Vavilov in Saratov, where he got a teacher at the university. Soon the future academician published a study on plant stability to infections in which first indicated the genetic properties of immunity.
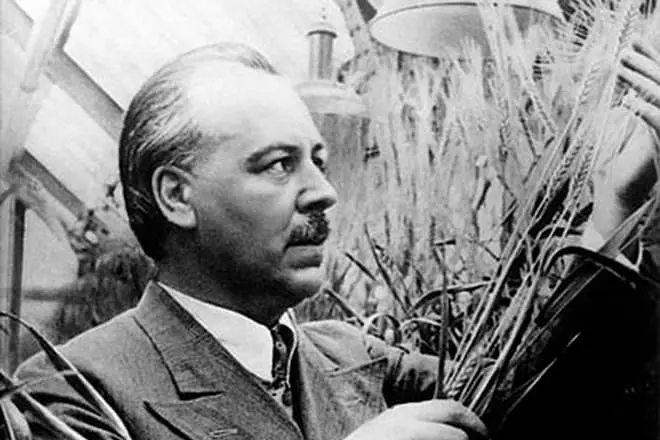

The opening of the Professor Soviet biologists learned in the 1920s at the Congress of breeders in Saratov. The scientist report shed light on the basis of the theory of variability. Colleagues Nikolai Ivanovich called the opening of Vavilov corresponding to the scale of the discovery of Dmitry Mendeleev in the chemistry and opening the broadest prospects for practice.
A year later, Nikolai Vavilov outlined the law of homologous series in America, at the International Agricultural Congress. The report of Vavilov called the sensational, portraits of the Soviet scientist decorated the editors of newspapers.

Later, after the publication by Nikolai Vavilov, research on the centers of origin of cultivated plants, scientists received a kind of compass, allowing to navigate in the boundless plant world of the Earth.
In 1921, Nikolai Ivanovich was invited to Petrograd, where he with a group of students and like-minded people organized the All-Union Institute of Creeding. The university, located in the royal village, passed the twenty recent years of the life of the famous scientist.
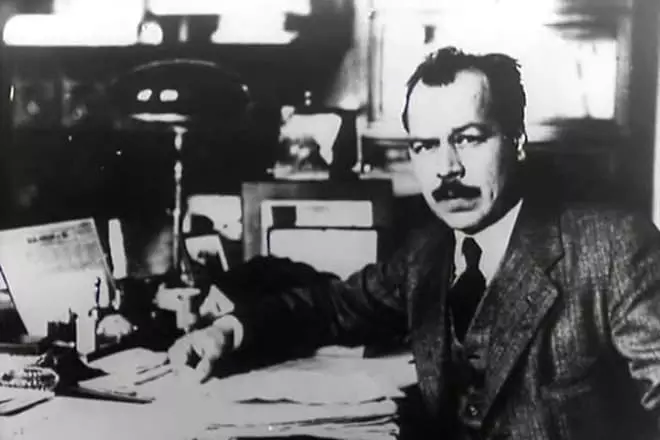

In 1929, Nikolai Vavilov becomes academician and President Vaschnil. The 42-year-old president settled contacts with colleagues from America and Europe. Soviet genetics in the 1930s and the first half of the 40s goes one step ahead of Western science.
Biological expedition
Half of the life of Vavilov took place in expeditions. In the student, the young scientist proceeded to the Caucasus tent and the North Caucasus.
In the 1920s, the scientist is a recognized leader of the Soviet biology and the luminaries of agrarian science - reinforced the opening and development of the richest material, which was collected together with students in scientific expeditions.
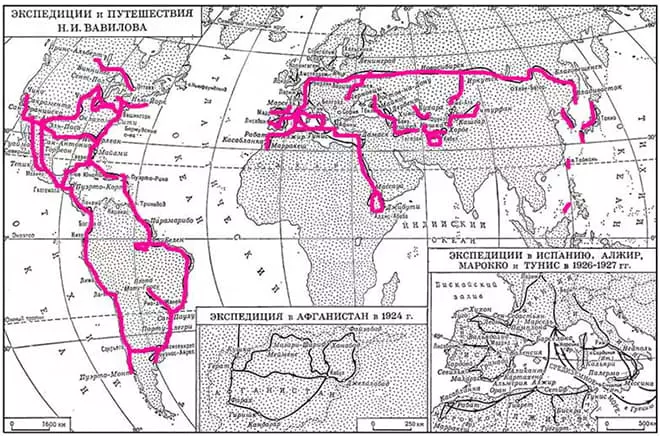
In 1924, Professor visited Nuristan - closed for Europeans of the province of Afghanistan. Foreign expeditions in the Mediterranean, Africa and India incredibly enriched the collection of seeds. The scientist wrote that in India "found a prazhi" and "Gindukush translated four times, once along the path of Alexander Macedonsky."
In the mid-1920 hedes, he visited an expedition to the Hivinsky Oasis of Uzbekistan, and in 1926-27 he conducted research work in Algeria, Morocco, Syria and Palestine. Nikolay Vavilov studied Greece's floral world, south of France, circulated Spain and Portugal. The hiking routes of Vavilov and his groups amounted to 2 thousand kilometers, and the collected material consisted of thousands of samples.
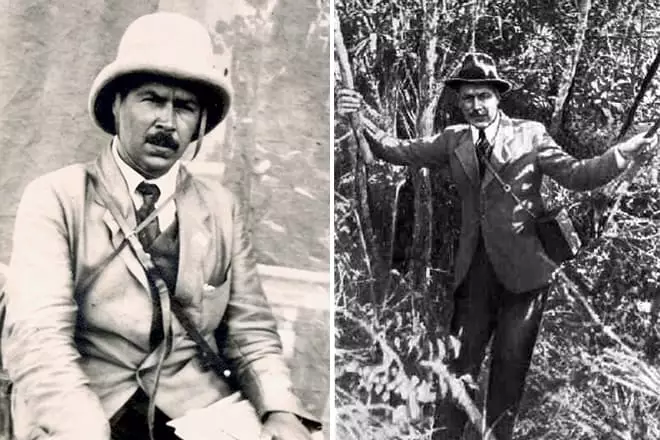

In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the scientist visited Japan, China and South America. After expeditions, his second most important work on the centers of origin of cultivated plants was published, for which V. I. Lenin award was awarded.
Nikolai Ivanovich for a brief life committed 180 expeditions in America and Eurasia, who enriched world science and brought him the Lavra of the Great Traveler. The result of expeditions was the richest collection of cultivated plants, which has reached 250 thousand samples in 40 years and has become the world's first Gennel Bank.
Personal life
Vavilov's classmates at the Agricultural Academy were surprised at the agricultural academy, having learned about the courtships of the clever and handsome Nikolai for the student Katya Sakharov. Catherine is the daughter of the Siberian merchant, no beauty, "blue stocking", string and dry in communication. But Nikolai Vavilov fell in love with a girl for her sharp mind. With Katya, he spoke all themes. They got close to practice in the Poltava province. Married in 1912. No wedding travel speech went about - in those years, the future academician already lived in the "Vavilovsky" mode: frequent business trips and multi-month expeditions, exhausting work in an inhuman pace - the fifth of the day was given to sleep.
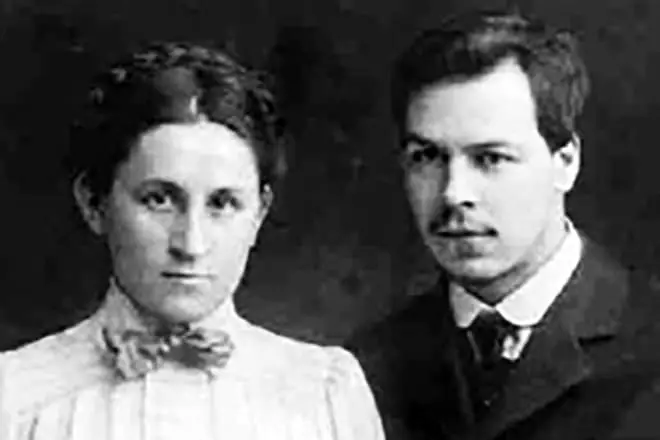

In the father's house at the middle forehead, where the couple settled, the cabinet window glows until the morning.
The Sr. Vavilov did not accept the October Revolution and emigrated to Bulgaria in 1918. A few days after the departure, the former merchant Ivan Ilyich Vavilov became a grandfather: Nikolai and Catherine had a first-mentioned Oleg. Grandfather saw the grandson in 1928, before his death. Nikolai Ivanovich persuaded his father to return to Russia, and a week later, Ivan Vavilov died.
The personal life of Nikolai Vavilov and Ekaterina Sakharov did not work out. After the birth of the son, the scientist went to work in Saratov. Katya with a little son stayed in Moscow. A year later, the husband got an apartment, and the family reunited. But Vavilov had another woman. With Elena Barulina, the scientist met on the expedition. The graduate student without memory fell in love with the professor of the agronomic faculty, older for 8 years.
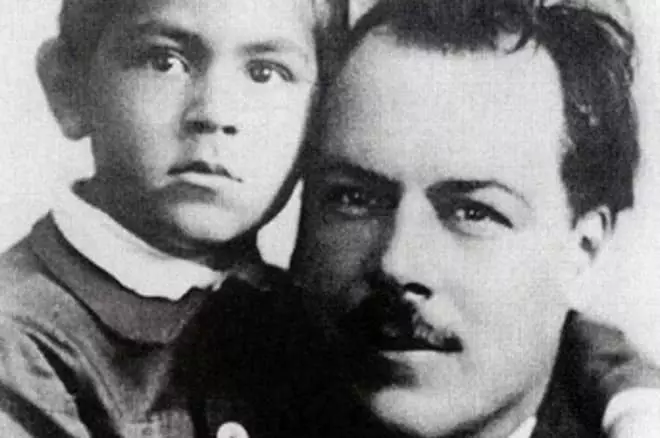

Nikolai Vavilov tried to save a family: in 1921, having moved to Leningrad, he called his wife with his son. But Catherine refused, realizing that the place in the heart of her husband was busy. The woman remained in Saratov, then returned to Moscow, where she lived with his son Oleg in the house at the middle forehead.
On Elena Barulina Nikolai Vavilov married in 1926. Two years later, the Son of Yuri was born in the spouses.

The sons of Vavilov became physicists. Oleg Vavilov, graduating from MSU, worked as a researchers of the Laboratory of Cosmic Rays. In December 1945, after the death of his father, defended his thesis. He died in 1946 in Dombay, where he went with a group of climbers.
Yuri Vavilov graduated from the University of Leningrad, where he studied at the Faculty of Nuclear Physics - a specialty closed for children of "enemies of the people."
Arrest
The regional authorities in the 1920s, in the 30s Nikolai Vavilov felt the ring compressing around him. From the institute of crop production, Vavilov's nearest associates were expelled.
In 1929, the repressions were tightened: non-partisan engineers, scientists, agricultural and economists called "right-matteists" and "pests", were arrested by the OGPU and were shot. Nikolai Vavilov petitioned for many colleagues, whose authority did not allow the authorities to take himself for a long time.

The fateful role in the tragic fate of the academician played Trofim Lysenko. The young agronoma from the people at the beginning of the 30th Academician Vavilov supported, although noted that it was not necessary to count on instant positive results from the progressable Lysenko of the Surrium (exposure to low temperatures on the development of the plant).
The young scientist liked Joseph Stalin "People's" origins and promises to achieve an incredible grain yield for the year and a half. When, at the congress of collective farmers - drummers in 1935, Trofim Lysenko said that "pests in science", and the collective farmers "give a folk economy more than some professors", Joseph Vissarionovich approvally exclaimed "Bravo, Comrade Lysenko!".
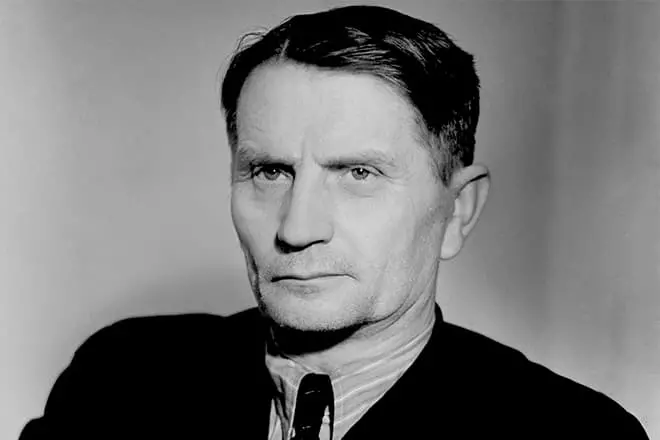

In 1938, Trofim Lysenko became president of Vavilov, replacing Vavilov in this post. From 1939, with the support of Stalin, Lysenko with supporters robbed genetics, calling the bourgeois lzhenauka industry.
In the summer of 1939, the associate and right hand of Trofim Lysenko - Isaac Israelich Present - Posted by the chairman of the USSR Council, Vyacheslav Molotov, a memorandum in which Nikolai Vavilov and his colleagues who were preparing the VII International Genetic Congress. The present suggested that Congress will become a "means of struggle against advanced science."
The VII International Congress took place, but not in the Union, but in Scotland. Nikolai Vavilov did not receive permission for departure, and the chair of the chair on the stage was empty.
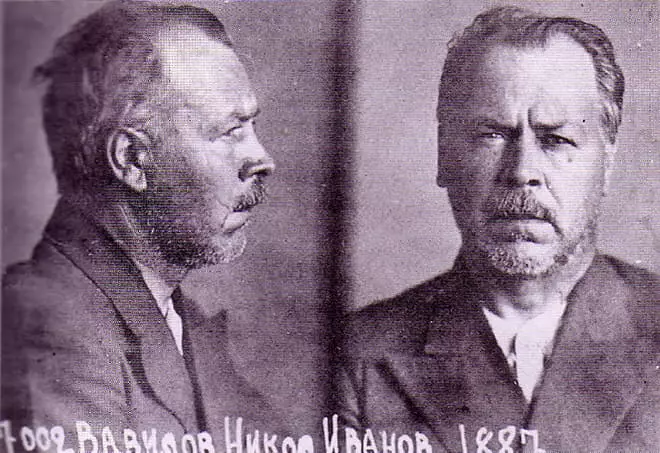

In August 1940, Nikolai Vavilov, who was in the scientific expedition in Chernovtsy, arrested. The investigation lasted 11 months. The scientist was called for interrogation of 400 times, and the cumulative interrogation time lasted 1700 hours. The investigation was the staff of the NKVD Alexey Vrashat and Sultan Albogachius. Especially "tried" a semi-faceted grip, which used torture torture to Vavilov.
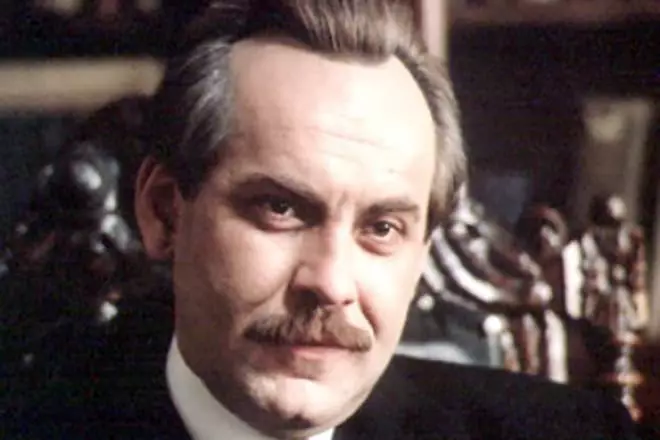

In 2000, the director Alexander Pokhkin said in 2000 on the events of the 1940s in the Drama "Nikolay Vavilov". Vavilova played Kostas Smororigas, as Trofim Lysenko and his comrades of Isaac Present spectators saw Bogdan Metha and Sergey Gazarov.
Death
The health of Vavilov, torture and hunger, who has undermined in expeditions, torture and hunger, caused the death of a scientist. The canceled death sentence did not change anything into the fate of the academician. In Saratov prison, the exhaust and dystrophy suffer Nikolai Vavilov fell ill with inflammation of the lungs. Due to the decline of cardiac activity on January 26, 1943, death came.
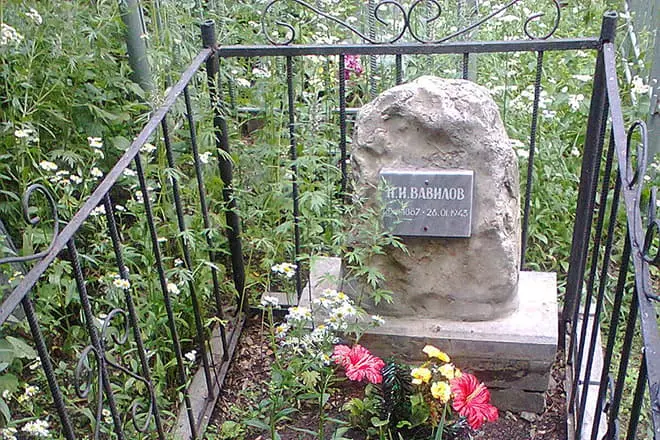

The Great Scientist was buried in a common grave for prisoners, the exact burial place is unknown. On the Resurrection Cemetery of Saratov, an individual grave and a monument to Vavilov installed.
Interesting Facts
- By the beginning of the Great Patriotic War, founded by Vavilov in the Tsarskoye Village, the plant of crop production owned the most huge collection of seeds in the world. During the blockade, the Institute staff retained a collection in the absence of electricity and interruptions with heating.
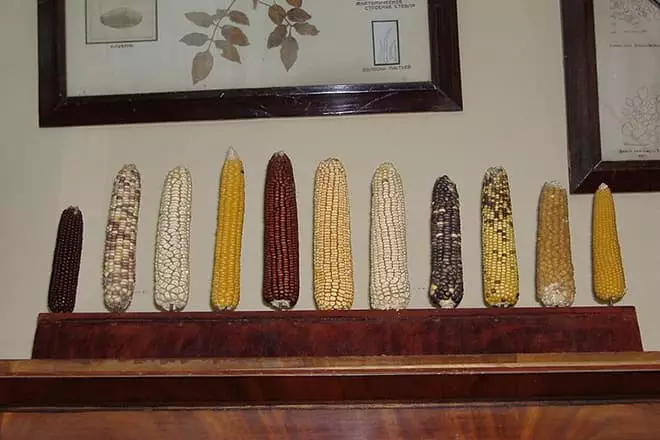

- In winter, 1941-1942, five institute staff died from hunger, refused to consider the stocks of cereals as food. In the summer, scientists planted seeds under artillery shelling.
