Biography
Contribution to the science of Claudia Ptolemy is impossible to overestimate. Proceedings of a scientist in the field of astronomy, physics, mathematics, geography and even the music of the world, if not fundamental, then, at a minimum, gave impetus to the development of these sciences. The mass of literature came to this day about the achievements of the scientist, but there are no biographical information.
Ptolemy developed a detailed reference book on antique astronomy, which was published under the name "Almagest". This work of an ancient scientist became the "Bible of Astronomy" until the theory of Copernicus, which laid the beginning of science about heavenly bodies.

The latitude of scientific interests and the depth of the analysis allowed Ptolemy to become the founder of scientific literature in the field of geography, physics (optics), music theory, etc. The theory is also developed by Claudia, according to which the celestial bodies are constantly moving and functioning as one mechanism.
The doctrine of the stars and their influence on the fate of a person, called astrology, also developed Ptolemy. He created an astronomical atlas, in which the constellations visible from the territory of Egypt.
Childhood and youth
Information about the biography of an ancient scientist has not been preserved. This is due to the fact that contemporaries avoided mention of Ptolemy in their writings. All available information is drawn from the books of Physics Physics Physics, as well as from its own scientific works of an ancient scientist. It is known that Claudia lived on the territory of modern Egypt, in the city of Alexandria. Information on the appearance of the scientist is also not preserved, the photo is a certain extent of the image from the works of ancient sculptors.

In the book "Almagest" Ptolemy indicates periods of astronomical observations, which help indirectly establish the dates of the scholar's life: 127-151 years. However, after the end of the work on the "Almagest", at least at least two books appeared, which are encyclopedias, work on which lasted for another 10 years. And according to the records of the philosopher of Olympiodore, Claudius worked close to Alexandria in the city of Cane - suburb of Alexandria Abukir.
Although the name of the scientist (Ptolemy) speaks about the Egyptian origin, and biographical information is about belonging to people from Greece, the first name (Clavdy) indicates the Roman roots of its owner. Due to the lack of reliable information, establish the nationality of the scientist is not possible.
Science and opening
The scientific activity of Ptolemy began from work under the name "Canopic inscription", which is carved on a stonecase in the city of Canopy (suburb of Alexandria in Egypt) Astronomical parameters. Later, stele was destroyed, but information applied to it was preserved due to ancient Greek manuscripts.
Specifying a number of information, Claudius developed "Head Tables" - something like an astronomical reference book. In the theory of geocentrism, this information acted as evidence of Earth's immobility and movement around her other celestial bodies.

Before the world-famous Almagesta, Ptolemy worked for another number of scientific books, including "planetary hypotheses". The difference between this work on others is the other parameter system used to describe the location of astronomical objects. In this treatise, the term Aristotle "Ether" appears, which is tightly woven into the theory of Ptolemy.
In Almagest Ptolemy, with an amazing accuracy for those times, the distance from the Sun and the Moon to Earth calculated. The measurement unit in the studies was the radius of the Earth. However, in the same "planetary hypotheses", the author pointed out the distance between the sun and other planets, without having their radius (instead, the scientist used the following conclusion: the radius of the planet is minimally equal to the distance from it to the next object of the visible universe), which may indicate the discrepancy between spelling periods scientific works.
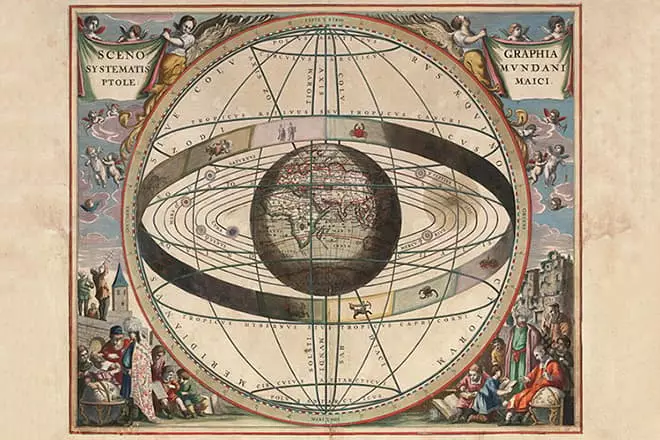
The next book, according to researchers, was the work of the "phase of fixed stars". This work is the first attempts to compile meteorological forecasts of the weather, based on the position of heavenly bodies and physical phenomena on the surface of the planet. In the same paper, the knowledge of the climatic zones and geographical belts of the Earth, as well as the mutual arrangement of geographical objects, was reduced.
To create astronomical theories, Ptolemia needed geometric knowledge of our planet. The theorem of the calculation of radii, arcs and circles is devoted to the work of Claudia called "Analema". The applied value of these knowledge is to design the solar clocks, which were built long before Ptolemy studies. The work of "Plasferey" is devoted to the stereographic projection and its use in astronomical calculations.
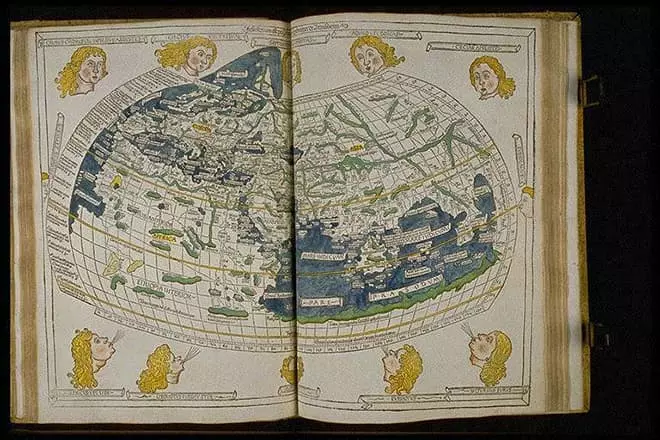
"Quadripartituum" became the most ambiguous work of Claudia, since it is devoted to the basics of astrology, or the influence of the heavenly bodies for a person's life. But the eight-grader "Geography" in popularity is not inferior to Almagesta. It is not so much descriptive geography as mathematical with the basics of cartography. In the first volume, the scientist suggested that the point of reference from the zero meridian, which was then served by the Canary Islands.
Disputes and discussions regarding the contribution of Ptolemy to science is still underway, on the basis of the fact that Hipparh long before Claudia described the positions of heavenly luminaries in the sky. The first falsification of the data found the poet Omar Khayam. And with the advent of Copernicus on the International Scientific Arena, the astronomical teachings of Ptolemy and became irrelevant at all. And only Jordan Bruno developed the theory of geocentrism for some time, supporting an ancient scientist in his beliefs. However, soon the geocentric system of the universe was refuted by other scientists.
Personal life
On a married position, as well as the presence of either the absence of children in Claudia, reliable information has not been preserved. But it is just known that the scientist had followers and assistants who helped him to make great discoveries in science. The Astronomical Book "Almagest" Ptolemy dedicated to Sira, but his personality is not established, who he had to scientist and whether the attitude towards his research or astronomy is generally unknown.
In the same treatise, the Mathematician Theon is mentioned, the data of which was used by clawdies in astronomical calculations, but was the theon teacher of Ptolemy or a colleague is also unknown.

A number of researchers suggest that we are talking about the theone of Smirnsky - a philosopher, follower of Plato, who also studied the starry sky and made a primitive map of the night skyscle.
COLLIADIAL PERSONAL Relations were at Claudia and with the staff of the Scientific Library in the Alexandria of Egypt, since he received access to the necessary literature unhindered. In historical sources of the beginning of our era, Claudia tied with the Egyptian dynasty of Ptolemyev, but modern researchers tend to consider this coincidence.
Death of Ptolemy
Circumstances and date of death of a scientist, like all the facts of his biography, remain a mystery so far. The opinion of the majority of researchers is reduced to the fact that the date of death of Claudia should be considered 165 years of our era.

According to archival information, during this period in the territory of Africa and Eurasia, the epidemic of the plague, the victim of which, possibly became Ptolemy. But even three thousand years after death, the scientist continues to live in his writings and benefit the descendants.
Bibliography
- "Canopian inscription"
- "Prudial Tables"
- "Planetary hypotheses"
- "Phases of fixed stars"
- "Analym"
- "Plasferey"
- "Quartrointhe"
- "Geography"
- "Optics"
- "Harmonics"
- "On the ability of judgment and decision making"
- "Fetus"
- "Gravity" and "Elements"
