Biography
Mathematics scientist Alan Turing in the text of the work "On computable numbers", published in 1936, proved that there is no universal method of establishing truth and cannot be in mathematical science. Mathematics will always contain non-permitting tasks. The works of Turing affecting this problem are recognized as the basis for academic studies in the field of artificial intelligence.Childhood and youth
Alan Matison Turing was born in Maida Vale, London, June 23, 1912. School teachers recognized the extraordinary mental abilities of Alan, but did not attach importance to them. The boy visited the prestigious school of the city of Shernborne, where it was particularly interested in accurate sciences. In the biography of the scientist contains a number of interesting facts. The first day of the young man's school accidentally coincided with the start of the strike, and he was forced to overcome 100 km on a bike, to spend the night in the hotel in accommodation, away from the rebellious crowd.

After Sherbourne, Turing entered the number of students of the Royal College (University of Cambridge), where he studied for three years. According to the results of the protection of master's work, in which Alan proved the central limit theorem, the young man is enrolled in the staff of teachers.
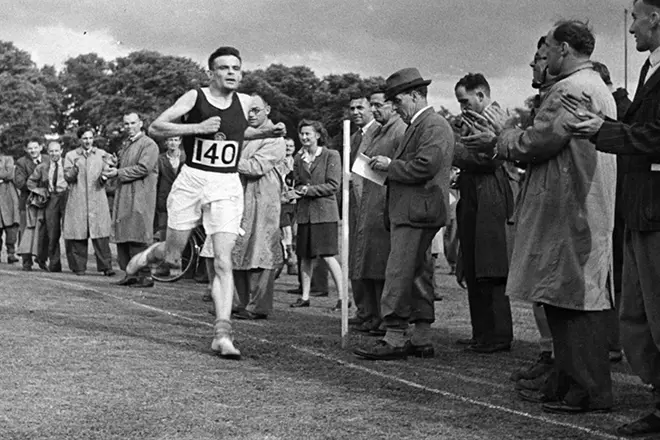
Young Alan, though he gave the science all the time and had an image of an eccentric among his colleagues, he was engaged in sports - in British archives, 1946 was preserved in the British archives, where the young man ran the marathon.
The science
In 1936, the work of Turing "On Computable Numbers" was published, in the text of which Alan introduced the concept of a universal machine (later it is called the Turing machine). Turing Machine calculated everything that is possible, the concept of a modern personal computer is based on a project developed by Turing.

Then, Turing focused on the study of mathematics and cryptology based on the Institute of Prospective Research in Princeton, New Jersey. After the protection of the doctoral dissertation in Princeton University in 1938, a young scientist returned to Cambridge, where she got a part-time work at the Center for Government Communications - a British government organization that worked on the breakdown of ciphers.
Personal life
1952 year. Turing opened the door and froze on the threshold of his apartment: everything is turned upside down in the rooms, the bottom of the furniture is income. At the owner's table, a note was waiting for a warning that if Turing would turn to the police, his intimate mystery will reveal to the whole world. The fact that a brilliant scientist is gay was not yet known. The scientist did not choke himself and still called the guards of the order. The hacker turned out to be a familiar lover Alan. But the problem of robbery went to the background, when the police found a confirmation of the unconventional sexual orientation of the man in the apartment.

In the early 1950s, homosexuality in the United Kingdom was illegal, so when Turing was admitted to the police that he had sexual relations with the criminal, 19-year-old Arnold Murrey, the scientist was accused of rude obscenity. After the arrest of Turing was forced to choose between forced treatment with hormonal drugs to reduce libido or imprisonment. Alan chose the first and soon subjected to chemical castration through the injections of the synthetic hormone estrogen during the year, which ultimately made it impotent.
As a result of the publicity of the sexual orientation of the scientist, he was forbidden to continue working with cryptography in GCCS.
The Second World War
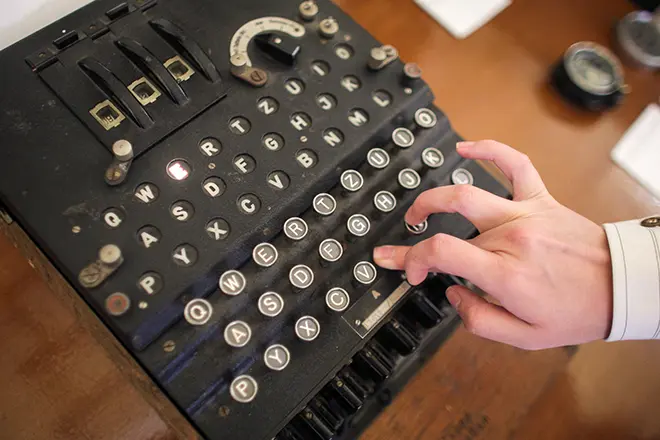
During World War II, Turing became the leading participant in the decoding of German ciphers. He worked at Bletchley Park, at the Military Time Station GCCS, where he made five major discoveries in the field of cryptanalysis, including the development of an electromechanical device used in order to decipher the signals of the English encryption machine "Enigma". The work released by Alan Turing, and dedicated to the decryption "Enigma", his colleagues called the "Book of the Profa" (the phleg called him for the eyes himself).

The contribution of Turing in the process of hacking codes is not limited to this: Alan also wrote two articles about mathematical approaches to code decryption, which are considered strategically important assets of the Cypher Code and School (later known as government headquarters). The Center for Government Communication only in April 2012 published these developments in the National Archive of the United Kingdom of Great Britain.
By the end of the war, Turing moved to London, where he worked in the National Physical Laboratory. Among the notable contributions of Alana to science for the period of work, it is worth noting that Turing is supervised by the design of an automatic computing mechanism and, ultimately, developed an innovative computer plan with relevant software products.
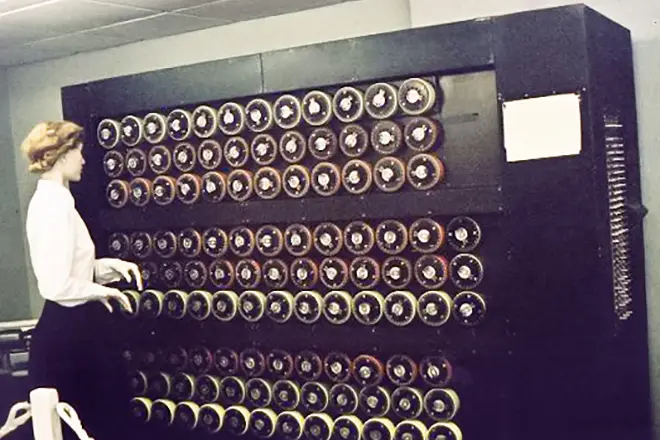
Although the full version of ACE was not designed, its concept was used as a model technological corporations around the world for several more years, having an impact on the design of the British Electric Deuce and American BENDIX G-15, which are considered the world's first personal computers.
Turing a certain time still held high-ranking positions in the Mathematics Department and in the University's Computational Lab in Manchester. For the first time, he studied the problem of artificial intelligence in the 1950 article "Computing equipment and exploration" and proposed an experiment known as the Turing Test - an attempt to create a standard for developing intelligence information for the technical industry. Over the past decades, the test has had a noticeable effect on the discussion about artificial intelligence.
Death of Alan Tyurring
Having lost opportunities to work in science, Turing fell into depression. In addition, against the background of receiving hormonal drugs, a man began to fall out, died appetite and sexual attraction, began to grow breasts.

Turing died on June 7, 1954. Mrs. Christie (Housekeeper Alan) prepared the owner of breakfast and climbed into the bedroom to call Turing on the table, but he discovered the scholar body into bed in bed, and there was an overhaul on her bedside table. After the posthumous examination, it turned out that the cause of death was poisoning cyanide.
Near the body found apple residues, although no parts of the apple were found in the stomach. The autopsy showed the "liquid content in the stomach, which strongly smelled of bitter almonds, as well as a solution of cyanide." In other organs, the smell of bitter almond was also noted. The autopsy showed that the cause of death was asphyxia due to cyanide poisoning. Suicide has been announced by the official version.

In the June article of the BBC, Professor of Philosophy and Expert on Turing Jack Copeland, argued that the death of Turing, perhaps, became an accident: cyanide in apples is not contained, nothing in the records of the last days of Turing on the thoughts on suicide, but Alan House has a cyanide for chemical experiments.
However, another version is also known. When the Second World War is over, Turing worked on the decrypt of Soviet ciphers. Researchers suggest that the KGB agents staged a robbery in the apartment of a scientist and led him to a trap, as a result of which the work on decoding of Soviet codes was stopped. And other scientists of such a level, to continue the work of Turing, there was no time in the UK.
Awards
- Excellent Order of the British Empire
- London Royal Society
Memory
- On September 10, 2009, the British Prime Minister Gordon Brown rehabilitated the outstanding compatriot Alan Tyurring.
- The term "computer" The modern world is obliged to Alan Turing.
- The prestigious premium for contributing to computer science (250 thousand dollars) is the name of Turing.
- According to one of the versions, the apple (Apple emblem) became a tribute to a genial scientist from Steve Jobs.
- The life of a brilliant scientist is reflected in the film "The game of imitation", where the role of Turing was played by the British actor Benedict Cumberbatch.
