Biography
Jean Calvin - French Theologian, one of the representatives of the flow of reformation, the philosopher, as well as the founder of his own teaching, called "Calvinism". The life of this man was not simple, but the purposefulness and loyalty to their views made Jean Calvin a noticeable figure of that time.Childhood and youth
The future theologians and the reformer was born on July 10, 1509 in a pious Catholic family. Kalvin's homeland is Nuayon's city, which is in the northern part of France. The boy's father achieved impressive success as secretary of the local bishop, as well as a fiscal prosecutor.
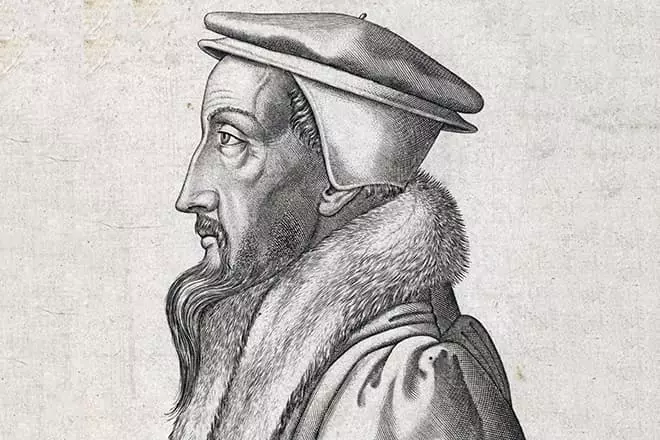

Jean's mother died when he was still a child, and his father had lacking time to raise his sibling. Therefore, Little Jean was given under the custody of one plenty family, where he received the basics of education and absorbed the Great Matters.
At the age of 14, Jean Calvin at the insistence of his father went to Paris to learn the right and humanitarian science. Over the years of study, the young man podnataroval in dialectics and became an intelligent speaker. Few later young man even trusted to read the sermons in one of the church parishes. Then, reaching majority, Calvin (again, following the will of the Father) continued to education.

This time, the young man began to comprehend the wisdom of jurisprudence, and graduating his studies, moved to Orleans, where he entered the students to the famous lawyer Pierre Stelle. Despite the obvious success on this field and constant praise of famous mentors, immediately after the death of Father, Jean Calvin leaves jurisprudence and appeals to theology.
The young man studied the works of the saints, on which Christian faith, the Bible, its numerous interpretations and comments on it. Already at that time, Jean Calvin took possession of the "cleansing" of the church. Parallel Calvin received a scientific degree of licentia and preached in two small arrival.
1532 In the biography of Jean Calvin was marked by two events: the young man received a doctoral degree, as well as on his own funds issued the first scientific treatise. These were comments to the work of the Sveti philosopher under the name "About meekness".
It is worth noting that the character of Jean was to become the hobbies of a young man: in 23 years it was a rather unlike man, immersed in his own ideas and ready to defend the views that seemed to him the only true. Jean peers even gave that nickname "accumulative", that is, the "accusative case", and were constantly called the "moralist."
Doctrine
Gradually, Jean Calvin penetrated with reformal ideas. Great influence, in the opinion of biographers and historians, Martin Luther (the founder of reformal views) was rendered to the worldview of Theologian (founder of reformal views).

In addition, the young man was not alien to the postulates of Humanism Erasmus Rotterdam and Lefevra d'Etapl. At about the same time, in Paris, a peculiar community of supporters of reformational views began to form, to which Calvin joined, and soon thanks to the oratoritious abilities and was at all the leader of this group.
The main task of contemporaries and the Christian society as a whole, Jean Calvin considered the elimination of the abuse of clergy, which were frequent. Also, the main teachings of Calvin were based on the idea of equality of all people in front of God and worldly law. The reformer did not scare the counteraction of clergy, he even decided to spread his unsuitable speech "On Christian Philosophy" in print.

Such liberty attracted the attention of the authorities who covered their eyes to the Mzduchiism of church servants and were not interested in the termination of such vicious practices. Jean Calvin has been persecuted, the reformer began to search for across Paris. For a while, a man was covered by like-minded people, and then Calvin moved to Geneva, where he planned to spend only night.
However, these plans were destined to change: in Geneva Calvin also met followers and found a friend and assistant in the face of the preacher and theology of the Gilome of Fineel. The efforts of the latter, Jean Calvin became known in Geneva, where he was delayed contrary to the initial plans. Soon about the new teaching, which already received the name "Calvinism" already at the time, it became known far beyond the limits of Geneva.

Some time later, Calvina had to leave this hospitable city for the same reason as the native country. Theologians moved to Strasbourg - a city in which most residents adhered to Protestantism. The devotee and there found a lesson, preaching and reading lectures in one of the cathedrals.
Soon, Strasbourg spoke about the new reformer, and Calvin received the official place and sorry for the preacher, which greatly facilitated his daily life. In 1537, already returned to Geneva, Jean Calvin graduated from the large-scale work "Catechism" - a peculiar set of laws and postulates of "Calvinism", addressed to both churchmen and the secular population.
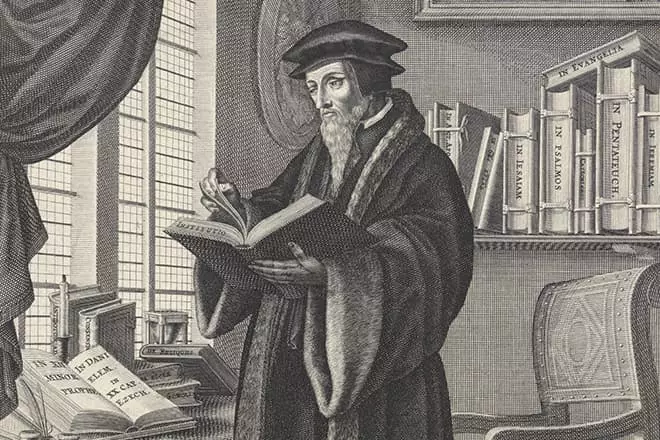

These rules turned out to be strict and demanded a guidance of new orders in the city, but the city council supported the reformer, and Catechism approved at the next meeting. However, the undertaking, which seemed to be good, soon turned into a severe dictatorship.
During the time in Geneva, in fact, the rules Jean Calvin and his supporters are powered by dozens of death sentences. No less citizens were expelled outside the hometown, the rest lived in constant fear of the local court and the authorities: at that time, torture was considered ordinary phenomenon, and the fears of citizens had a serious soil.

In parallel, Jean Calvin worked on the most serious work in life, called "instruction in the Christian faith." This large-scale work became a collection of books, sermons, lectures and essays that reveal the views of the author, instructions to contemporaries and future generations. Total Calvin wrote 57 volumes.
The main thought, the central motive, the next through the works of Jean Calvin, is to recognize the Supreme Divine power to everyone. The sovereignty of God, according to Calvin, means the fullest human subordination to the Lord's will.
Only one choice is available to people - to be with God or renounce the faith and persecute yourself on terrible flour after the earthly life. However, this choice, considered Calvin, is predetermined in advance by God. With age, the reformer became more delicious, harsh and intolerable to dissent.
Personal life
Jean Calvin was married. In 1540, the theologian was combined with a woman with a woman named Idetetta de Bur.
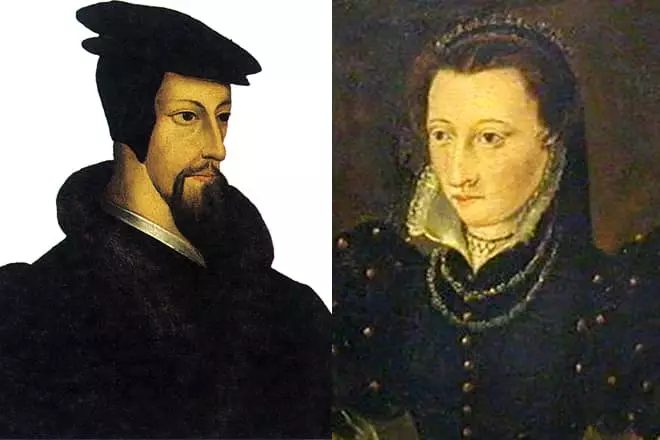

The spouse gave the reformer of three children, but they all died in infant age, without allowing Calvin to experience the happiness of the parent. It is known that Calvin's wife left his life before him.
Death
In 1559, Jean Calvin picked up the strongest fever, but abandoned the beddown and continued active activity. After some time, the disease retreated, but the health of the theologian was seriously shaken.

In 1564, during the next sermon, Calvin fell as a ragged, the man's mouth went. Three months, the reformer spent in bed in terrible torments, and on May 27, 1564, Jean Calvin did not.
Proceedings
- 1536 - "Insertions in the Christian faith"
- 1543 - "Treatise on relics"
