Biography
Roman doctor of Claudius Galen made a tremendous contribution to the development of science. In his biography, a lot of "dark spots", and from the treatises survived hardly a quarter, but this did not prevent several years to consider its achievements as axioms. Even the unwitting mistakes of Galen, until the Renaissance, was considered irrefutable truths, and his works predetermined the development of Western medicine for the 15th centuries ahead.Childhood and youth
Galen was born in 131 in Pergamma, the city in Malaya Asia (now it is Turkish Bergama), in the era of the board of Emperor Adriana. Researchers tend to the conclusion that Claudius is not a personal name, but the wrong decoding of the Clarissimus title is "nice", which was added to the name of the author in medieval manuscripts.

The future doctor was born in a secured and educated family. Nikon's father has heard a prominent thinker and a connoisseur of mathematics, so he paid close attention to the teaching of the Son, dreaming that he would make a famous philosopher from him in one day. According to the legend, change the decision and give Galen to learn medicine. He made him forced the prophetic dream - at that time, the Romans gave these things with great importance and considered such events direct leadership to action.
Medicine and scientific activities
Galena's medicine was taught prominent Pergham scientists, including Anatas Satir and Pathologist Strothonik. When the Father died, the young man went on a trip to Smyrna to take over the experience of local doctors. There he continued the study under the leadership of the famous Pelops - the author of the theory of respiratory relationship with blood circulation. That first used the word "aura" (from the Greek "light wind"), believing that the air substance moves inside the body by vessels. Later, Galen visited Corinth, where he studied the science of drugs and natural science, and then in Alexandria, where he entered the disciples to Anomat Heraklion.

At that time, Alexandria walked the center of medical science, and the young doctor dreamed of discovering unique knowledge and experienced professionals there. However, by the time Galen arrived there, the law came out, prohibiting the preparation of human bodies, and the anatomy had to be studied on monkeys and other mammals.
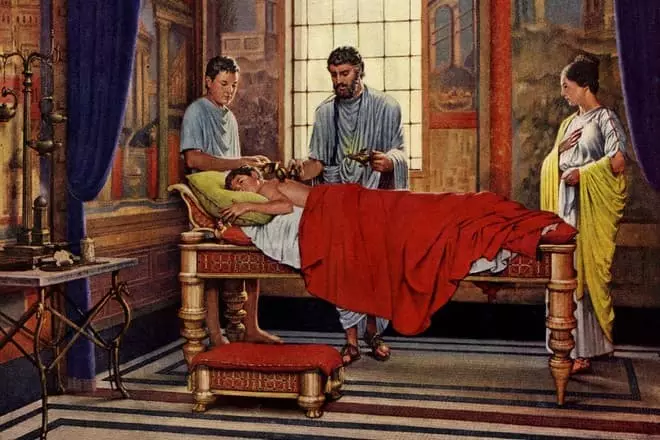
Galen returned home disappointed. Having dedicated to traveling for 6 years, he settled in his native Parchment. By the time the doctor was 29 years old. He entered the scene of the surgeon to the school of gladiators and the next 4 years honed the art of refueling dislocations, sewing RAS and the treatment of fractures. The work was hard, comparable to everyday military-field surgeons, only without modern equipment, medicines and anesthesia.
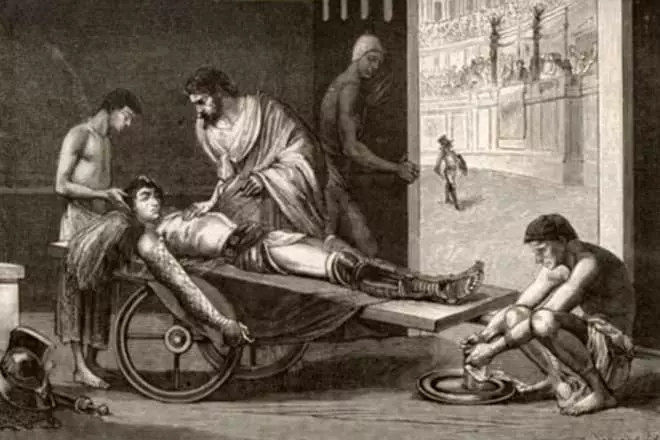
Scene Galen deserved after demonstrated his ability to operate on a monkey's corpse. The state of the health of the wards was given the closest attention: injuries that the doctor called the "body windows", gave the opportunity to receive an idea of anatomy. During his work, only 5 gladiators died, while his predecessor buried 60.
When in 164 the uprising broke out in the city, the 33-year-old doctor moved to the capital. There he quickly gained popularity, not only as a doctor, but also as an experienced lecturer. His fame Galen was largely obliged to philosopher EVDEM - he cured that from severe illness, and the grateful thinker glorified him throughout Rome as a skillful physician.

Soon Galen presented to the emperor Mark Abrenie and instructed to lecture on the anatomy in the temple of the world. The course was visited not only by physicians, but also other citizens interested in science, including representatives of the highest aristocracy, for example, consul-louges north and relatives of Emperor Barbar.
Despite the external success, Galen in Rome lived difficult, first of all because of his own nature. He was an active and pretty vain person, everywhere sought to draw attention to himself, because of what the envious and enemies would be easy. In the end, when the dislike of colleagues to the "starning" became unbearable, Galen left Rome and went to travel in Italy.

He returned only after 2 years on the personal call of the emperor. Mark Aureliy ordered him to appear in a military camp in Aquilee and gathering himself, but the doctor managed to persuade the emperor to leave him at home. By that time, the fear of the enemies became in Galen obsessive: he endlessly changed the place of residence and lived in a constant alarm.
As a result, he settled in the palace as a personal physician of the emperor. He appreciated his approximate - Galen not only helped him overcome frequent malaise, but also entertained by philosophical conversations. Heaped he and Commoda, the heir to Mark Aurelia, who was then killed as a result of the court conspiracy.

The consciousness of its superiority and fear of the enemies (mostly ghostly) all this time did not leave the proud Galen. From the rivals, he appreciated only one colleague. Asclepads Vhyphic, who studied at Cleophon and who lived in Athens, was famous for the talent and sanity and sought to eradicate the solar and harmful traditions of treatment, and his only Galen considered it equal to himself.
The famous epidemic is also connected with the name of the doctor, called Chuma Galen, then Antoninovsky Chuma (according to the name of the emperor-owned then). The manuscripts recorded an unusually long nature of the dissemination of the disease.

The opinions of researchers about how many lives have taken an epidemic, differ - figures are mentioned from 7% to 50% of the population. The records of the distribution and nature of the disease of the brief and are unisexitive, but from the fact that Galen documented, it can be assumed that the taste of the Ose virus, and not the plague.
Gallen outlined their views and ideas in detail in treatises, the most famous of which are considered "anatomy" and "On the appointment of parts of the human body". Most of the work was kept in the temple of the world and, unfortunately, burned down during a fire in the Palatian library.
Its noticeable contribution to science was the foundation of etiology. Galen divided into categories known by the time of the disease, described and systematized their causes (he divided the factors to solid, apparent, liquid, etc.), and also pointed out the connection of pathogenic effects with the condition of the body - according to the doctor, the internal reasons "prepared the soil »For the development of the disease.
Galen became one of the first who began to apply an experimental approach in biology. The famous medic practiced vivisection, animal experiences, developed a skull opening technology. A valuable discovery was the discovery and description of the nervous trunk and spinal cord. An interesting fact - many scientists believe that due to the legislative ban Galen for the whole practice, did not make a single autopsy of the human body.

His knowledge in the anatomy was limited to information obtained as a result of the opening of bodies of cows, monkeys and pigs, and because of this sinned frequent errors. He recognized the limit of his own experience, pointing to it in the records.
The total number of manuscripts of Galen is estimated as close to 400, although only half of them were medical - until later, he retained the passion of philosophy and willingly reasoned the topics on abstract topics. About 100 treatises have been preserved to this day, of which the new names of bodies, bones and other anatomical concepts were drawn. In his writings, Galen replaced the common, but the names of the gippocrat's names with their own terms with contemporaries.

The Roman physician is also considered the father of pharmacology. Some of the described recipes, such as Raddkrem, called "Galenic Prepares" are used in medicine and cosmetology to this day.
The place of Galen in medicine has long remained exceptional. His merits were imperatively exceeded up to the 14th century, and the views retained the authority until the Middle Ages, thoroughly breeding the Galenism, which ruled among scientists and was canonized by the Church. Only in the era of Renaissance, there was a person who decided to unsubscribe the old ideals and achievements and point out the inaccuracy of the existential ideas - they were Paracels.
Personal life
The mention is not preserved about his wife and children of the great doctor. Perhaps in his difficult, rich in events and wanders, fate simply did not find time for personal life, but perhaps contemporaries in their memories simply missed this information as an insignificant.

Galen considered himself a highly moral man and sharply condemned the fall of morality among the Roman doctors, comparing them with the robbers and consider that the entire difference between them consists only that some commit crimes in the mountains, while others in the capital.
"The mind of most doctors is directed not to science, not for useful recipes, he wrote angrily. - Low borestolubie makes them capable of any post-act. "Death
Together, the famous doctor returned to his homeland in Pergami to devote himself to work on manuscripts. He died in the era of the reign of septimia of the North. The exact cause of death is unknown, but by the time the scientist was already in old age - according to different estimates, he was then 70, whether 87 years old.
